Survival, recurrence and toxicity of HNSCC in comparison of a radiotherapy combination with cisplatin versus cetuximab: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 27565887
- PMCID: PMC5002133
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2706-2
Survival, recurrence and toxicity of HNSCC in comparison of a radiotherapy combination with cisplatin versus cetuximab: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Cisplatin-based treatment has been considered the standard treatment regimen of HNSCC. Cetuximab is an emerging target therapy that has potential therapeutic benefits over cisplatin. Nevertheless, curative effects of cisplatin-based chemoradiotherapy (CRT) versus cetuximab-based bioradiotherapy (BRT) are still controversial.
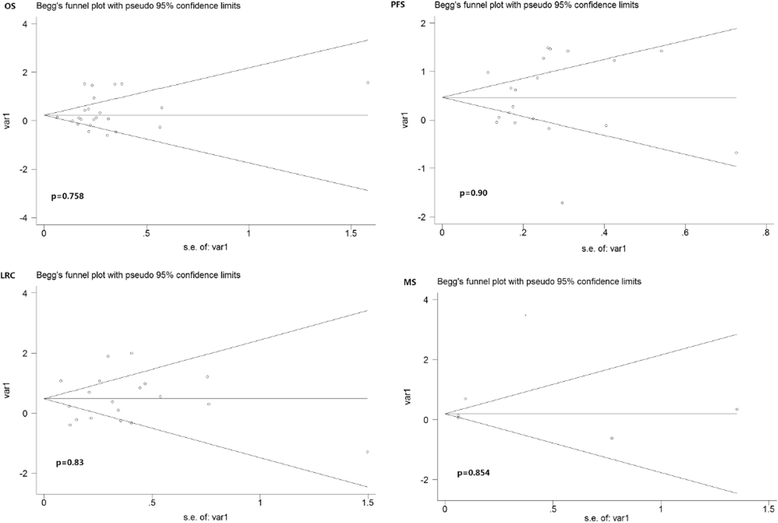
Methods: Potentially eligible studies were retrieved using PubMed, Embase and Medline. Basic characteristics of patients and statistical data were collected. A meta-analysis model was established to compare CRT and BRT.
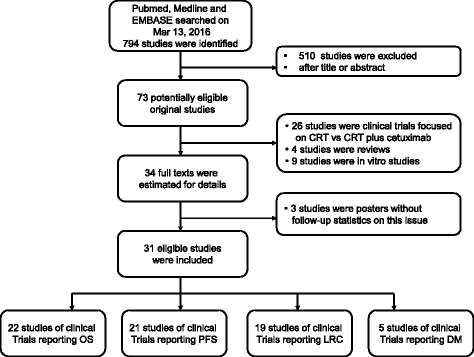
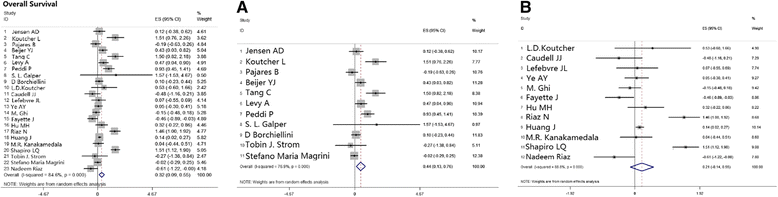
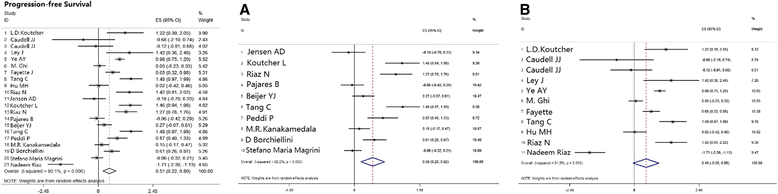
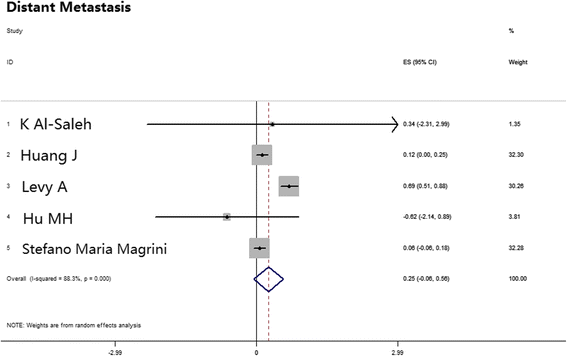
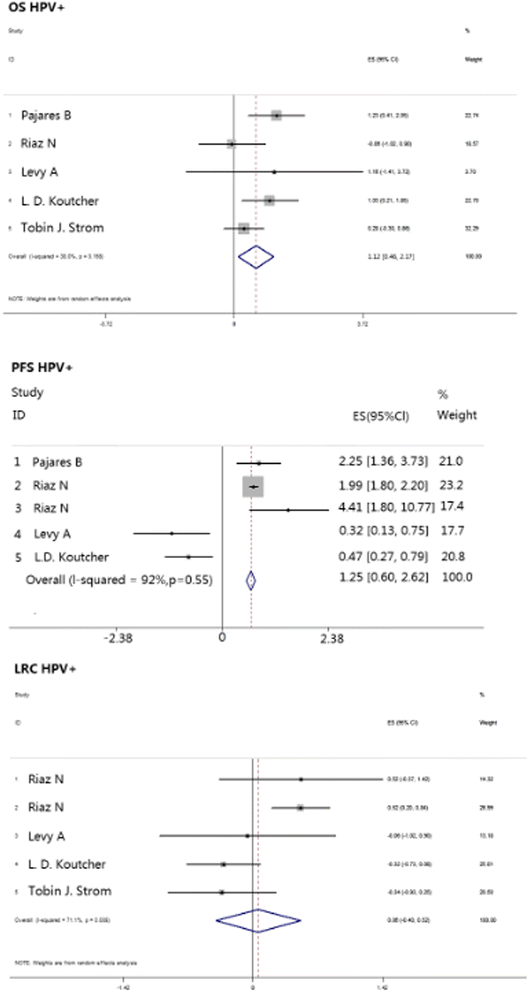
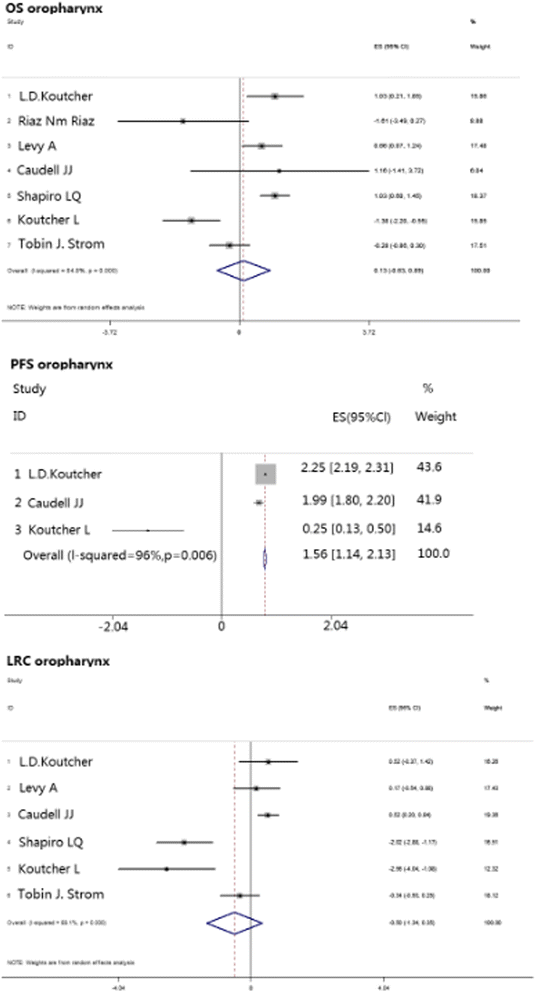
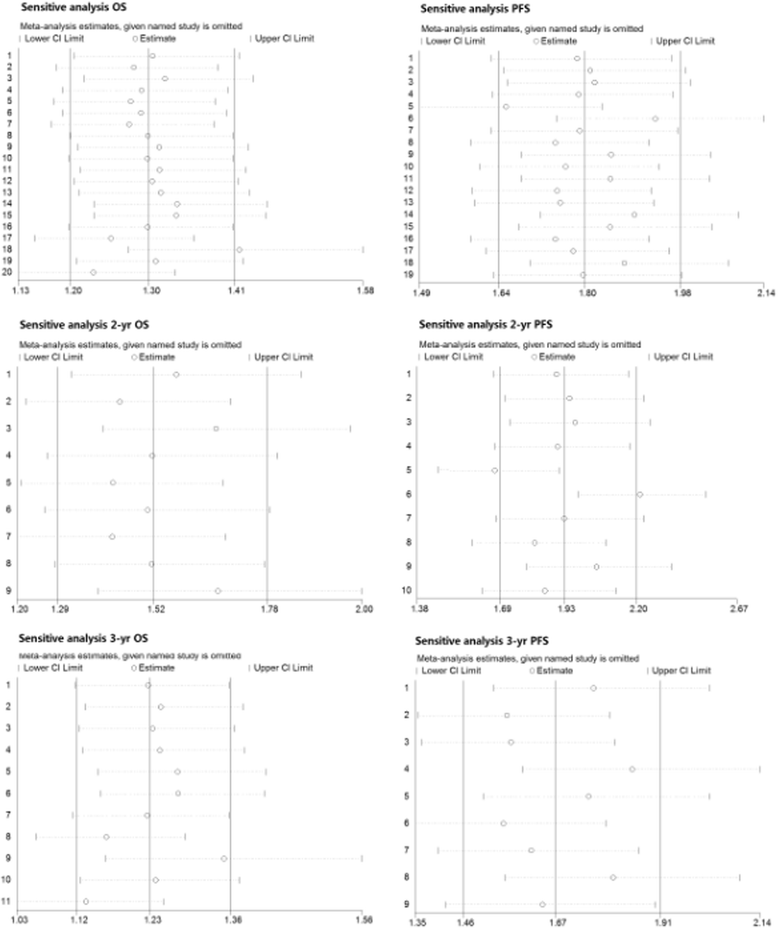
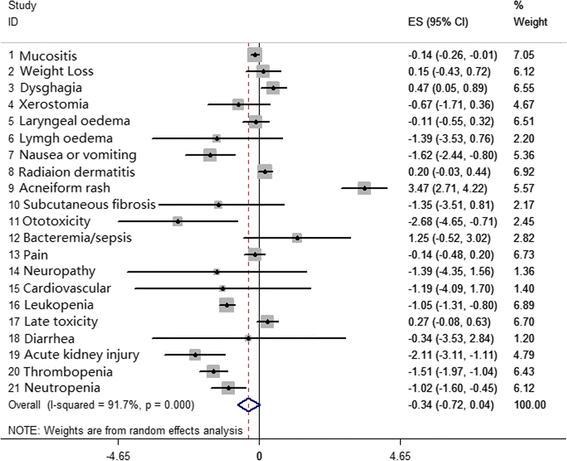
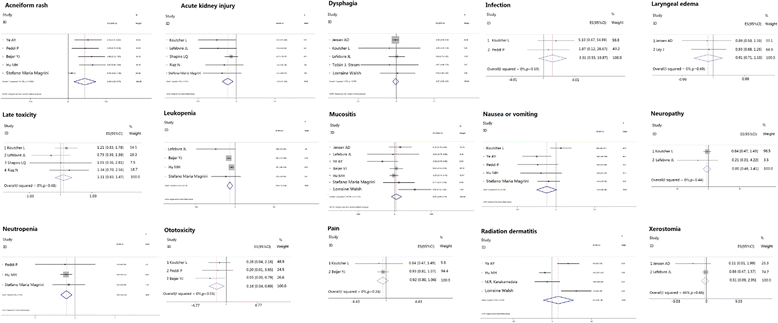
Results: Thirty-one eligible studies and 4212 patients were found. The pooled HRs with 95 % confidence intervals (CIs) for OS and PFS were 0.32 [0.09, 0.55] and 0.51 [0.22, 0.80], respectively, and both were in favor of cisplatin. However, 3-year survival and recurrence analysis of the subgroups showed no differences between the two groups (p > 0.05). In subgroup analysis, oropharyngeal primary tumors exhibited improved results by cetuximab with a pooled HR of 1.56 [1.14, 2.13] for PFS. Additionally, the HPV+ status was a significant factor in positive outcomes with cetuximab with a pooled HR of 1.12 [0.46, 2.17] for OS.
Conclusion: Long-term use of BRT showed no significant difference compared with CRT, and both arms showed different aspects of toxicity. In subgroup analysis, taking the effects of treatment and adverse events into consideration, cetuximab plus radiation may show superior responses regarding OS and PFS in patients who have HPV+ or primary oropharyngeal HNSCC, respectively, but physicians should administer them with caution.
Keywords: Adverse event; Cetuximab; Cisplatin; HNSCC; HPV; Oropharynx; Prognosis; Radiotherapy; Recurrence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Concurrent cisplatin or cetuximab with radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Sep 4;99(36):e21785. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021785. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32899005 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent chemoradiotherapy with cisplatin or cetuximab for locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: Does human papilloma virus play a role?Oral Oncol. 2016 Aug;59:50-57. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.05.019. Oral Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27424182
-
Comparison of acute toxicities associated with cetuximab-based bioradiotherapy and platinum-based chemoradiotherapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: A single-institution retrospective study in Japan.Acta Otolaryngol. 2015 Aug;135(8):853-8. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2015.1030772. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Acta Otolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 25814008
-
Concurrent use of cisplatin or cetuximab with definitive radiotherapy for locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Strahlenther Onkol. 2014 Sep;190(9):823-31. doi: 10.1007/s00066-014-0626-0. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Strahlenther Onkol. 2014. PMID: 24638267
-
The Effect of Induction Chemotherapy Using Docetaxel, Cisplatin, and Fluorouracil on Survival in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis.Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Jul;48(3):907-16. doi: 10.4143/crt.2015.359. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 26582394 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Myofascial Induction Therapy Improves the Sequelae of Medical Treatment in Head and Neck Cancer Survivors: A Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Cross-Over Study.J Clin Med. 2021 Oct 27;10(21):5003. doi: 10.3390/jcm10215003. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34768520 Free PMC article.
-
ACLY (ATP Citrate Lyase) Mediates Radioresistance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas and is a Novel Predictive Radiotherapy Biomarker.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 7;11(12):1971. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121971. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31817870 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Physical Therapy Modalities on Quality of Life of Head and Neck Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2021 Oct 13;10(20):4696. doi: 10.3390/jcm10204696. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34682818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiomic-Based Molecular Landscape of FaDu Xenograft Tumors in Mice after a Combinatorial Treatment with Radiation and an HSP90 Inhibitor Identifies Adaptation-Induced Targets of Resistance and Therapeutic Intervention.Mol Cancer Ther. 2024 Apr 2;23(4):577-588. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-23-0796. Mol Cancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 38359816 Free PMC article.
-
Cetuximab-Containing Combinations in Locally Advanced and Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2019 May 20;9:383. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00383. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31165040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

