De novo ALK kinase domain mutations are uncommon in kinase inhibitor-naïve ALK rearranged lung cancers
- PMID: 27565908
- PMCID: PMC5002311
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.06.006
De novo ALK kinase domain mutations are uncommon in kinase inhibitor-naïve ALK rearranged lung cancers
Abstract
Introduction: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearranged lung adenocarcinomas are responsive to the multitargeted ALK inhibitor crizotinib. One of the common mechanisms of resistance to crizotinib is the acquisition of ALK kinase domain mutations. However, the presence of ALK mutations in crizotinib-naïve tumors has not been widely reported and it is unclear if de novo ALK mutations affect the response to crizotinib.
Methods: We analyzed preclinical models of ALK rearranged lung cancers that were sensitive/resistant to ALK inhibitors, probed our institutional and other lung cancer databases for tumors with ALK kinase domain mutations, and evaluated tumor response to crizotinib.
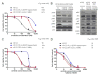
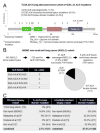
Results: ALK rearranged cell lines with ALK kinase domain mutations were heterogeneously less inhibited by increasing concentrations of crizotinib than cells driven solely by EML4-ALK fusions. Previous ALK rearranged lung cancer cohorts did not report ALK kinase mutations in inhibitor-naïve tumors. We identified one TKI-naïve ALK rearranged tumor with an ALK kinase domain mutation: ALK-S1206F (mutations at ALK-S1206 shifted crizotinib inhibitory curves only minimally in preclinical models). The never smoker whose tumor harbored de novo EML4-ALK-E5;A20+ALK-S1206F only achieved a 4-month radiographic response to crizotinib 250mg twice daily.
Conclusions: Combining data from our and prior cohorts, ALK kinase domain mutations were uncommon events (<3% of cases) in ALK inhibitor-naïve ALK rearranged lung adenocarcinomas but their effect on intrinsic resistance to ALK inhibitors should be better evaluated.
Keywords: ALK; Adenocarcinoma; Crizotinib; Kinase domain; Lung cancer; Mutation.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
STATEMENT Daniel B. Costa has received consulting fees and honoraria from Pfizer Inc (unrelated to the current work), consulting fees from Ariad Pharmaceuticals (unrelated to the current work), and honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim (unrelated to the current work). Antonio R. Lucena-Araujo, Jason P. Moran, Paul A. VanderLaan, Dora Dias-Santagata, Erik Folch, Adnan Majid, Michael S. Kent, Sidharta P. Gangadharan, Deepa Rangachari, Mark S. Huberman, and Susumu S. Kobayashi have no conflicts to disclose. No other conflict of interest is stated.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dual ALK and EGFR inhibition targets a mechanism of acquired resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor crizotinib in ALK rearranged lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2014 Jan;83(1):37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.09.019. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Lung Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24199682 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of resistance to crizotinib in patients with ALK gene rearranged non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 1;18(5):1472-82. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2906. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22235099 Free PMC article.
-
ALK inhibitors in the treatment of advanced NSCLC.Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 Mar;40(2):300-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014. PMID: 23931927 Review.
-
K-RAS mutations indicating primary resistance to crizotinib in ALK-rearranged adenocarcinomas of the lung: Report of two cases and review of the literature.Lung Cancer. 2016 Mar;93:55-8. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.01.002. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Lung Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26898615 Review.
-
Heterogeneity of genetic changes associated with acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2013 Apr;8(4):415-22. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318283dcc0. J Thorac Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23344087 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
The Landscape of ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Clinicopathologic, Genomic Characteristics, and Therapeutic Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 29;14(19):4765. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194765. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary resistance to first- and second-generation ALK inhibitors in a non-small cell lung cancer patient with coexisting ALK rearrangement and an ALK F1174L-cis-S1189C de novo mutation: A case report.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 23;13:1060460. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1060460. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36506539 Free PMC article.
-
ALK inhibitors in cancer: mechanisms of resistance and therapeutic management strategies.Cancer Drug Resist. 2024 May 23;7:20. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.25. eCollection 2024. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38835344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Refining Criteria for Choosing the First-Line Treatment for Real-World Patients with Advanced ALK-Rearranged NSCLC.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 21;26(13):5969. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135969. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Relevance of an Amplicon-Based Liquid Biopsy for Detecting ALK and ROS1 Fusion and Resistance Mutations in Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.JCO Precis Oncol. 2020 Apr 2;4:PO.19.00281. doi: 10.1200/PO.19.00281. eCollection 2020. JCO Precis Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32923908 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

