A phase I trial of the Hedgehog inhibitor, sonidegib (LDE225), in combination with etoposide and cisplatin for the initial treatment of extensive stage small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 27565909
- PMCID: PMC5427482
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.04.014
A phase I trial of the Hedgehog inhibitor, sonidegib (LDE225), in combination with etoposide and cisplatin for the initial treatment of extensive stage small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Objectives: The Hedgehog pathway has been implicated in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) tumor initiation and progression. Pharmacologic blockade of the key Hedgehog regulator, Smoothened, may inhibit these processes. We performed a phase I study to determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of sonidegib (LDE225), a selective, oral Smoothened antagonist, in combination with etoposide/cisplatin in newly diagnosed patients with extensive stage SCLC.
Materials and methods: Patients received 4-6 21-day cycles of etoposide/cisplatin with daily sonidegib. Patients with response or stable disease were continued on sonidegib until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Two dose levels of sonidegib were planned: 400mg and 800mg daily, with 200mg daily de-escalation if necessary. Next generation sequencing was performed on available specimens. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) were quantified at baseline and with disease evaluation.
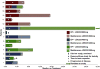
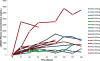
Results: Fifteen patients were enrolled. 800mg was established as the recommended phase II dose of sonidegib in combination with etoposide/cisplatin. Grade 3 or greater toxicities included: anemia (n=5), neutropenia (n=8), CPK elevation (n=2), fatigue (n=2), and nausea (n=2). Toxicity led to removal of one patient from study. Partial responses were confirmed in 79% (11/14; 95% CI: 49-95%). One patient with SOX2 amplification remains progression-free on maintenance sonidegib after 27 months. CTC count, at baseline, was associated with the presence of liver metastases and after 1 cycle of therapy, with overall survival.
Conclusions: Sonidegib 800mg daily was the MTD when administered with EP. Further genomic characterization of exceptional responders may reveal clinically relevant predictive biomarkers that could tailor use in patients most likely to benefit.
Keywords: Circulating tumor cells; Hedgehog inhibitor; Hedgehog pathway; LDE225; SOX2 amplification; Small cell lung cancer.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A phase I study of pomalidomide (CC-4047) in combination with cisplatin and etoposide in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2013 Apr;8(4):423-8. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318282707b. J Thorac Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23370364 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I, multicenter, open-label, first-in-human, dose-escalation study of the oral smoothened inhibitor Sonidegib (LDE225) in patients with advanced solid tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Apr 1;20(7):1900-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1710. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24523439 Clinical Trial.
-
Cisplatin, Etoposide, and Bevacizumab Regimen Followed by Oral Etoposide and Bevacizumab Maintenance Treatment in Patients With Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Single-Institution Experience.Clin Lung Cancer. 2015 Nov;16(6):e229-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 May 18. Clin Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26072097
-
Expert opinion on sonidegib efficacy, safety and tolerability.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2021 Aug;20(8):877-882. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2021.1921734. Epub 2021 May 12. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2021. PMID: 33888008 Review.
-
Controversies in the treatment of advanced stages of small cell lung cancer.Front Radiat Ther Oncol. 2010;42:193-197. doi: 10.1159/000262476. Epub 2009 Nov 24. Front Radiat Ther Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19955807 Review.
Cited by
-
Hedgehog signaling mechanism and role in cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Oct;85:107-122. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.04.003. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 33836254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the tumor stroma for cancer therapy.Mol Cancer. 2022 Nov 2;21(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01670-1. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36324128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: clinical update.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015 Aug;12(8):445-64. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.61. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25850553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer stem cells: a major culprit of intra-tumor heterogeneity.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 15;11(12):5782-5811. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35018226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hedgehog/GLI Signaling Pathway: Transduction, Regulation, and Implications for Disease.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 7;13(14):3410. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143410. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34298625 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pepicelli CV, Lewis PM, McMahon AP. Sonic hedgehog regulates branching morphogenesis in the mammalian lung. Curr Biol. 1998;8:1083–1086. - PubMed
-
- Watkins DN, Berman DM, Burkholder SG, Wang B, Beachy PA, Baylin SB. Hedgehog signalling within airway epithelial progenitors and in small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2003;422:313–317. - PubMed
-
- Park KS, Martelotto LG, Peifer M, Sos ML, Karnezis AN, Mahjoub MR, Bernard K, Conklin JF, Szczepny A, Yuan J, Guo R, Ospina B, Falzon J, Bennett S, Brown TJ, Markovic A, Devereux WL, Ocasio CA, Chen JK, Stearns T, Thomas RK, Dorsch M, Buonamici S, Watkins DN, Peacock CD, Sage J. A crucial requirement for Hedgehog signaling in small cell lung cancer. Nat Med. 2011 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Travaglione V, Peacock CD, MacDougall J, McGovern K, Cushing J, Yu LC, Trudeau M, Palombella V, Adams J, Hierman J, Rhodes JT, Devereux WL, Watkins DN, A novel HH pathway inhibitor IPI-926, delays recurrence post-chemotherapy in a primary human SCLC xenograft model; 99th AACR Annual Meeting; San Diego, CA. 2008. p. 4611.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

