Meningiomas and Proteomics: Focus on New Potential Biomarkers and Molecular Pathways
- PMID: 27566655
- PMCID: PMC5070626
Meningiomas and Proteomics: Focus on New Potential Biomarkers and Molecular Pathways
Abstract
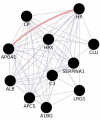
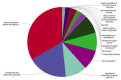
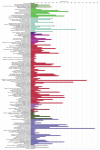
Meningiomas are one of the most common tumors affecting the central nervous system, exhibiting a great heterogeneity in grading, treatment and molecular background. This article provides an overview of the current literature regarding the molecular aspect of meningiomas. Analysis of potential biomarkers in serum, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and pathological tissues was reported. Applying bioinformatic methods and matching the common proteic profile, arising from different biological samples, we highlighted the role of nine proteins, particularly related to tumorigenesis and grading of meningiomas: serpin peptidase inhibitor alpha 1, ceruloplasmin, hemopexin, albumin, C3, apolipoprotein, haptoglobin, amyloid-P-component serum and alpha-1-beta-glycoprotein. These proteins and their associated pathways, including complement and coagulation cascades, plasma lipoprotein particle remodeling and lipid metabolism could be considered possible diagnostic, prognostic biomarkers, and eventually therapeutic targets. Further investigations are needed to better characterize the role of these proteins and pathways in meningiomas. The role of new therapeutic strategies are also discussed.
Keywords: Meningioma; bioinformatic analysis; protein pathways; proteomic.
Copyright© 2016, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. John G. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
