Gesture Performance in Schizophrenia Predicts Functional Outcome After 6 Months
- PMID: 27566843
- PMCID: PMC5049539
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbw124
Gesture Performance in Schizophrenia Predicts Functional Outcome After 6 Months
Abstract
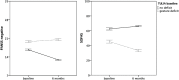
The functional outcome of schizophrenia is heterogeneous and markers of the course are missing. Functional outcome is associated with social cognition and negative symptoms. Gesture performance and nonverbal social perception are critically impaired in schizophrenia. Here, we tested whether gesture performance or nonverbal social perception could predict functional outcome and the ability to adequately perform relevant skills of everyday function (functional capacity) after 6 months. In a naturalistic longitudinal study, 28 patients with schizophrenia completed tests of nonverbal communication at baseline and follow-up. In addition, functional outcome, social and occupational functioning, as well as functional capacity at follow-up were assessed. Gesture performance and nonverbal social perception at baseline predicted negative symptoms, functional outcome, and functional capacity at 6-month follow-up. Gesture performance predicted functional outcome beyond the baseline measure of functioning. Patients with gesture deficits at baseline had stable negative symptoms and experienced a decline in social functioning. While in patients without gesture deficits, negative symptom severity decreased and social functioning remained stable. Thus, a simple test of hand gesture performance at baseline may indicate favorable outcomes in short-term follow-up. The results further support the importance of nonverbal communication skills in subjects with schizophrenia.
Keywords: hand gestures; negative symptoms; nonverbal communication; psychosis; social perception.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nonverbal social communication and gesture control in schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull. 2015 Mar;41(2):338-45. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbu222. Epub 2015 Feb 1. Schizophr Bull. 2015. PMID: 25646526 Free PMC article.
-
Nonverbal communication remains untouched: No beneficial effect of symptomatic improvement on poor gesture performance in schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2020 Sep;223:258-264. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2020.08.013. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Schizophr Res. 2020. PMID: 32883557 Free PMC article.
-
Is nonverbal communication disrupted in interactions involving patients with schizophrenia?Schizophr Bull. 2013 Sep;39(5):1150-8. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbs091. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Schizophr Bull. 2013. PMID: 22941744 Free PMC article.
-
Nonverbal behavior during face-to-face social interaction in schizophrenia: a review.J Nerv Ment Dis. 2014 Jan;202(1):47-54. doi: 10.1097/NMD.0000000000000031. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2014. PMID: 24375212 Review.
-
The revised NEUROGES-ELAN system: An objective and reliable interdisciplinary analysis tool for nonverbal behavior and gesture.Behav Res Methods. 2016 Sep;48(3):973-93. doi: 10.3758/s13428-015-0622-z. Behav Res Methods. 2016. PMID: 26428913 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurological Signs at the First Psychotic Episode as Correlates of Long-Term Outcome: Results From the AESOP-10 Study.Schizophr Bull. 2021 Jan 23;47(1):118-127. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbaa089. Schizophr Bull. 2021. PMID: 32656567 Free PMC article.
-
Modality-specific dysfunctional neural processing of social-abstract and non-social-concrete information in schizophrenia.Neuroimage Clin. 2021;29:102568. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102568. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Neuroimage Clin. 2021. PMID: 33524805 Free PMC article.
-
Gesture deficits and apraxia in schizophrenia.Cortex. 2020 Dec;133:65-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2020.09.017. Epub 2020 Oct 3. Cortex. 2020. PMID: 33099076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensorimotor and Activity Psychosis-Risk (SMAP-R) Scale: An Exploration of Scale Structure With Replication and Validation.Schizophr Bull. 2021 Mar 16;47(2):332-343. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbaa138. Schizophr Bull. 2021. PMID: 33047134 Free PMC article.
-
Single Session Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Ameliorates Hand Gesture Deficits in Schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull. 2020 Feb 26;46(2):286-293. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbz078. Schizophr Bull. 2020. PMID: 31634401 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- van Os J, Kapur S. Schizophrenia. Lancet 2009;374:635–645. - PubMed
-
- Lang FU, Kösters M, Lang S, Becker T, Jäger M. Psychopathological long-term outcome of schizophrenia—a review. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2013;127:173–182. - PubMed
-
- Fett AK, Viechtbauer W, Dominguez MD, Penn DL, van Os J, Krabbendam L. The relationship between neurocognition and social cognition with functional outcomes in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2011;35:573–588. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

