The therapeutic efficacy of intensive medical therapy in ameliorating high-density lipoprotein dysfunction in subjects with type two diabetes
- PMID: 27567897
- PMCID: PMC5002094
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-016-0314-4
The therapeutic efficacy of intensive medical therapy in ameliorating high-density lipoprotein dysfunction in subjects with type two diabetes
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: The therapeutic efficacy of intensive medical therapy in ameliorating high-density lipoprotein dysfunction in subjects with type two diabetes.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Nov 9;15(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0362-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27829435 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: To determine whether 12 months of intensive medical therapy (IMT) improves HDL functionality parameters in subjects with type II diabetes (T2D).
Methods: Retrospective, randomized, and controlled 12-month IMT intervention trial that enrolled 13-subjects with T2D (age 51- years, fasting glucose 147 mg/dL, body mass index [BMI] 36.5 kg/m(2)) and nine healthy control (46-years, fasting glucose 90 mg/dL, BMI 26.5 kg/m2). Subjects with T2D underwent IMT and HDL functionality measures (pro-inflammatory index of high-density lipoprotein (pHDL)), paraoxonase one (PON1), ceruloplasmin (Cp), and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity were performed on samples at baseline and at 12-months following IMT.
Results: At baseline, pHDL index was significantly higher in subjects with T2D (p < 0.001) and apolipoprotein A-1 levels were significantly lower (p = 0.013) vs.
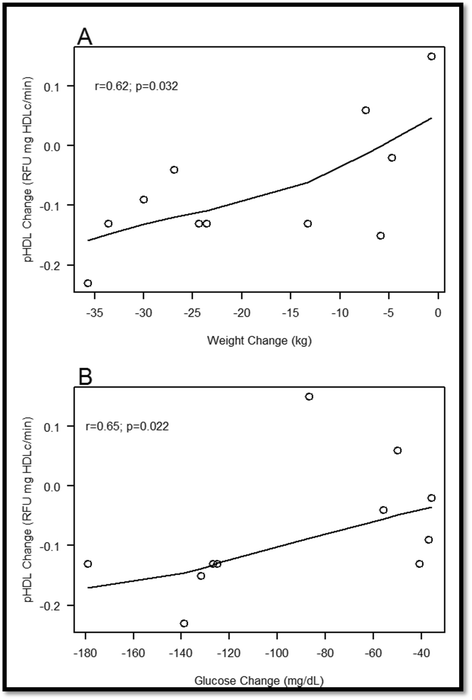
Controls: After 12-months, there was a trend for improved pHDL activity (p = 0.083), as indicated by intent-to-treat analysis, but when the non-adherent subject was omitted (per-protocol), significant attenuations in pHDL activity (p = 0.040) were noted; Δ pHDL activity at 12-months was associated with Δ weight (r = 0.62, p = 0.032) and Δ fasting glucose (r = 0.65, p = 0.022). Moreover, PON1 activity significantly improved (p < 0.001). The aforementioned occurred in association with improvements in inflammatory markers (i.e., C-reactive protein & tumor necrosis factor), hemoglobin A1C, fasting glucose, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein levels and adipokines.
Conclusion: IMT ameliorates pHDL index and significantly improves anti-oxidative function, as measured by PON1. Improvements in weight and fasting glucose mediated the decrease in pHDL index. Pharmacological aids and lifestyle modification are required to improve cardiovascular risk factors, subsequent mortality risk, and promote T2D remission. Application of either form of therapy alone may only have relatively miniscule effects on the aforementioned factors, in relation to the aggregate.
Keywords: Intensive medical therapy; Myeloperoxidase; Paraoxonase one; Pro-inflammatory high-density lipoproteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-density lipoprotein subspecies between patients with type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes without / with intensive insulin therapy.Endocr J. 2012;59(7):561-9. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.ej11-0329. Epub 2012 May 16. Endocr J. 2012. PMID: 22504174
-
Comparison of lipid profiles and lipoprotein a levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus during oral hypoglycemic or insulin therapy.Saudi Med J. 2006 Feb;27(2):174-80. Saudi Med J. 2006. PMID: 16501671
-
Modulating effect of atorvastatin on paraoxonase 1 activity in type 2 diabetic Egyptian patients with or without nephropathy.J Diabetes Complications. 2010 Sep-Oct;24(5):325-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2009.04.001. Epub 2009 Jun 23. J Diabetes Complications. 2010. PMID: 19553142 Clinical Trial.
-
Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes and its relationship to new therapeutic approaches.Diabetes Educ. 2000 Nov-Dec;26 Suppl:4-7. Diabetes Educ. 2000. PMID: 11912815 Review. No abstract available.
-
Why prescribe exercise as therapy in type 2 diabetes? We have a pill for that!Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2018 Jul;34(5):e2999. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2999. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29488311 Review.
Cited by
-
Erratum to: The therapeutic efficacy of intensive medical therapy in ameliorating high-density lipoprotein dysfunction in subjects with type two diabetes.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Nov 9;15(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0362-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27829435 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Alterations of HDL's to piHDL's Proteome in Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Diseases, and HDL-Targeted Therapies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 18;15(10):1278. doi: 10.3390/ph15101278. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycation Reduces the Stability of ApoAI and Increases HDL Dysfunction in Diet-Controlled Type 2 Diabetes.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Feb 1;103(2):388-396. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-01551. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 29077935 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review: the appraisal of the effects of metformin on lipoprotein modification and function.Obes Sci Pract. 2019 Jan 7;5(1):36-45. doi: 10.1002/osp4.309. eCollection 2019 Feb. Obes Sci Pract. 2019. PMID: 30820329 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

