Expandable and Rapidly Differentiating Human Induced Neural Stem Cell Lines for Multiple Tissue Engineering Applications
- PMID: 27569063
- PMCID: PMC5032182
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.07.017
Expandable and Rapidly Differentiating Human Induced Neural Stem Cell Lines for Multiple Tissue Engineering Applications
Abstract
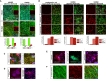
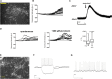
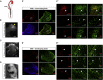
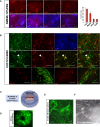
Limited availability of human neurons poses a significant barrier to progress in biological and preclinical studies of the human nervous system. Current stem cell-based approaches of neuron generation are still hindered by prolonged culture requirements, protocol complexity, and variability in neuronal differentiation. Here we establish stable human induced neural stem cell (hiNSC) lines through the direct reprogramming of neonatal fibroblasts and adult adipose-derived stem cells. These hiNSCs can be passaged indefinitely and cryopreserved as colonies. Independently of media composition, hiNSCs robustly differentiate into TUJ1-positive neurons within 4 days, making them ideal for innervated co-cultures. In vivo, hiNSCs migrate, engraft, and contribute to both central and peripheral nervous systems. Lastly, we demonstrate utility of hiNSCs in a 3D human brain model. This method provides a valuable interdisciplinary tool that could be used to develop drug screening applications as well as patient-specific disease models related to disorders of innervation and the brain.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Astrow S.H., Son Y.J., Thompson W.J. Differential neural regulation of a neuromuscular junction-associated antigen in muscle fibers and Schwann cells. J. Neurobiol. 1994;25:937–952. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y., Gaiarsa J.L., Tyzio R., Khazipov R. GABA: a pioneer transmitter that excites immature neurons and generates primitive oscillations. Physiol. Rev. 2007;87:1215–1284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

