Effects of RNAi-mediated knockdown of Xist on the developmental efficiency of cloned male porcine embryos
- PMID: 27569767
- PMCID: PMC5177977
- DOI: 10.1262/jrd.2016-095
Effects of RNAi-mediated knockdown of Xist on the developmental efficiency of cloned male porcine embryos
Abstract
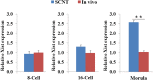
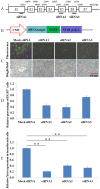
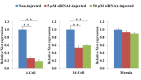
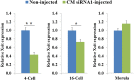
Xist is an X-linked gene responsible for cis induction of X chromosome inactivation. Studies have indicated that Xist is abnormally activated in the active X chromosome in cloned mouse embryos due to loss of the maternal Xist-repressing imprint following enucleation during somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT). Inhibition of Xist expression by injecting small interfering RNA (siRNA) has been shown to enhance the in vivo developmental efficiency of cloned male mouse embryos by more than 10-fold. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether a similar procedure can be applied to improve the cloning efficiency in pigs. We first found that Xist mRNA levels at the morula stage were aberrantly higher in pig SCNT embryos than in in vivo fertilization-derived pig embryos. Injection of a preselected effective anti-Xist siRNA into 1-cell-stage male pig SCNT embryos resulted in significant inhibition of Xist expression through the 16-cell stage. This siRNA-mediated inhibition of Xist significantly increased the total cell number per cloned blastocyst and significantly improved the birth rate of cloned healthy piglets. The present study contributes useful information on the action of Xist in the development of pig SCNT embryos and proposes a new method for enhancing the efficiency of pig cloning.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improvement of developmental competence of cloned male pig embryos by short hairpin ribonucleic acid (shRNA) vector-based but not small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated RNA interference (RNAi) of Xist expression.J Reprod Dev. 2019 Dec 18;65(6):533-539. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2019-070. Epub 2019 Oct 21. J Reprod Dev. 2019. PMID: 31631092 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi-mediated knockdown of Xist does not rescue the impaired development of female cloned mouse embryos.J Reprod Dev. 2013;59(3):231-7. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2012-195. Epub 2013 Jan 30. J Reprod Dev. 2013. PMID: 23363561 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi-mediated knockdown of Xist improves development of the female buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) nuclear transfer embryos.Theriogenology. 2022 Jul 15;187:27-33. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.04.020. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Theriogenology. 2022. PMID: 35500424
-
Effect of epigenetic regulation during swine embryogenesis and on cloning by nuclear transfer.Cell Tissue Res. 2010 Jul;341(1):13-21. doi: 10.1007/s00441-010-1000-x. Epub 2010 Jun 20. Cell Tissue Res. 2010. PMID: 20563602 Review.
-
[Progress on abnormal development of cloned pigs generated by somatic cell transfer nuclear].Yi Chuan. 2020 Oct 20;42(10):993-1003. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-105. Yi Chuan. 2020. PMID: 33229324 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Strategies to Improve the Efficiency of Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 10;23(4):1969. doi: 10.3390/ijms23041969. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
XIST Derepression in Active X Chromosome Hinders Pig Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer.Stem Cell Reports. 2018 Feb 13;10(2):494-508. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.12.015. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Stem Cell Reports. 2018. PMID: 29337117 Free PMC article.
-
Factors and molecules that could impact cell differentiation in the embryo generated by nuclear transfer.Organogenesis. 2017 Oct 2;13(4):156-178. doi: 10.1080/15476278.2017.1389367. Organogenesis. 2017. PMID: 29020571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockdown of YY1 Inhibits XIST Expression and Enhances Cloned Pig Embryo Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 23;23(23):14572. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314572. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36498896 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives in Genome-Editing Techniques for Livestock.Animals (Basel). 2023 Aug 10;13(16):2580. doi: 10.3390/ani13162580. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627370 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lyon MF. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature 1961; 190: 372–373. - PubMed
-
- Takagi N, Sasaki M. Preferential inactivation of the paternally derived X chromosome in the extraembryonic membranes of the mouse. Nature 1975; 256: 640–642. - PubMed
-
- Augui S, Nora EP, Heard E. Regulation of X-chromosome inactivation by the X-inactivation centre. Nat Rev Genet 2011; 12: 429–442. - PubMed
-
- Xue F, Tian XC, Du F, Kubota C, Taneja M, Dinnyes A, Dai Y, Levine H, Pereira LV, Yang X. Aberrant patterns of X chromosome inactivation in bovine clones. Nat Genet 2002; 31: 216–220. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

