MED12 Regulates HSC-Specific Enhancers Independently of Mediator Kinase Activity to Control Hematopoiesis
- PMID: 27570068
- PMCID: PMC5268820
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.08.004
MED12 Regulates HSC-Specific Enhancers Independently of Mediator Kinase Activity to Control Hematopoiesis
Abstract
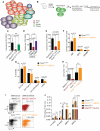
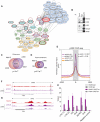
Hematopoietic-specific transcription factors require coactivators to communicate with the general transcription machinery and establish transcriptional programs that maintain hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) self-renewal, promote differentiation, and prevent malignant transformation. Mediator is a large coactivator complex that bridges enhancer-localized transcription factors with promoters, but little is known about Mediator function in adult stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. We show that MED12, a member of the Mediator kinase module, is an essential regulator of HSC homeostasis, as in vivo deletion of Med12 causes rapid bone marrow aplasia leading to acute lethality. Deleting other members of the Mediator kinase module does not affect HSC function, suggesting kinase-independent roles of MED12. MED12 deletion destabilizes P300 binding at lineage-specific enhancers, resulting in H3K27Ac depletion, enhancer de-activation, and consequent loss of HSC stemness signatures. As MED12 mutations have been described recently in blood malignancies, alterations in MED12-dependent enhancer regulation may control both physiological and malignant hematopoiesis.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
The Mediator of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Homeostasis.Cell Stem Cell. 2016 Dec 1;19(6):677-678. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.11.012. Cell Stem Cell. 2016. PMID: 27912086 Free PMC article.
-
MED12 in hematopoietic stem cells-cell specific function despite ubiquitous expression.Stem Cell Investig. 2017 Jan 18;4:3. doi: 10.21037/sci.2016.12.04. eCollection 2017. Stem Cell Investig. 2017. PMID: 28217705 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
There will be blood: hematopoiesis control by mediator subunit MED12.Stem Cell Investig. 2017 Jan 21;4:4. doi: 10.21037/sci.2016.12.02. eCollection 2017. Stem Cell Investig. 2017. PMID: 28217706 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Bringing light into gene regulation in hematopoietic stem cells by the Mediator complex.Stem Cell Investig. 2017 Feb 15;4:10. doi: 10.21037/sci.2017.01.04. eCollection 2017. Stem Cell Investig. 2017. PMID: 28275640 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Akoulitchev S, Chuikov S, Reinberg D. TFIIH is negatively regulated by cdk8-containing mediator complexes. Nature. 2000;407:102–106. - PubMed
-
- Beck D, Thoms JA, Perera D, Schütte J, Unnikrishnan A, Knezevic K, Kinston SJ, Wilson NK, O'Brien TA, Göttgens B, et al. Genome-wide analysis of transcriptional regulators in human HSPCs reveals a densely interconnected network of coding and noncoding genes. Blood. 2013;122:e12–e22. - PubMed
-
- Borggrefe T, Yue X. Interactions between subunits of the Mediator complex with gene-specific transcription factors. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011;22:759–768. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA173636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA133379/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA194923/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA149655/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA105129/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL048801/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK110805/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056465/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA169784/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 GM117302/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK106829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA190509/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

