CSF-1R inhibition attenuates renal and neuropsychiatric disease in murine lupus
- PMID: 27570219
- PMCID: PMC5326697
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.08.019
CSF-1R inhibition attenuates renal and neuropsychiatric disease in murine lupus
Abstract
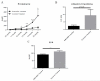
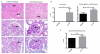
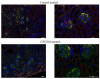
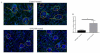
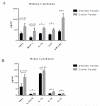
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multifactorial autoimmune disease that can affect multiple end organs. Kidney and brain are two of the organs most commonly involved in SLE. Past studies have suggested the importance of macrophages in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis (LN). Furthermore, as the immune effectors of the brain, microglia have been implicated in pathways leading to neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE). We depleted macrophages and microglia using GW2580, a small colony stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R) kinase inhibitor, in MRL-lpr/lpr (MRL/lpr) mice, a classic murine lupus model that displays features of both LN and NPSLE. Treatment was initiated before the onset of disease, and mice were followed for the development of LN and neurobehavioral dysfunction throughout the study. Treatment with GW2580 significantly ameliorated kidney disease, as evidenced by decreased proteinuria, BUN, and improved renal histopathology, despite equivalent levels of IgG and C3 deposition in the kidneys of treated and control mice. We were able to confirm macrophage depletion within the kidney via IBA-1 staining. Furthermore, we observed specific improvement in the depression-like behavioral deficit of MRL/lpr mice with GW2580 treatment. Circulating antibody and autoantibody levels were, however, not affected. These results provide additional support for the role of macrophages as a potentially valuable therapeutic target in SLE. Inhibiting CSF-1 receptor signaling would be more targeted than current immunosuppressive therapies, and may hold promise for the treatment of renal and neuropsychiatric end organ disease manifestations.
Keywords: CSF-1R; Lupus nephritis; Macrophages; Neuropsychiatric lupus; SLE.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Is Dependent on Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 26;9:2189. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02189. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30319641 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage depletion ameliorates nephritis induced by pathogenic antibodies.J Autoimmun. 2015 Feb;57:42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2014.11.007. Epub 2014 Dec 29. J Autoimmun. 2015. PMID: 25554644 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropsychiatric disease in murine lupus is dependent on the TWEAK/Fn14 pathway.J Autoimmun. 2013 Jun;43:44-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Autoimmun. 2013. PMID: 23578591 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of macrophages in lupus nephritis.Discov Med. 2015 Jul-Aug;20(108):43-9. Discov Med. 2015. PMID: 26321086 Review.
-
The MRL/lpr mouse strain as a model for neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:207504. doi: 10.1155/2011/207504. Epub 2011 Feb 10. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21331367 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
To Kill a Microglia: A Case for CSF1R Inhibitors.Trends Immunol. 2020 Sep;41(9):771-784. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Trends Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32792173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JHU-083 selectively blocks glutaminase activity in brain CD11b+ cells and prevents depression-associated behaviors induced by chronic social defeat stress.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Mar;44(4):683-694. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0177-7. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30127344 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL13 Neutralization Attenuates Neuropsychiatric Manifestations in Lupus-Prone Mice.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 12;12:763065. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.763065. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34868008 Free PMC article.
-
The CD6/ALCAM pathway promotes lupus nephritis via T cell-mediated responses.J Clin Invest. 2022 Jan 4;132(1):e147334. doi: 10.1172/JCI147334. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 34981775 Free PMC article.
-
Proliferation and Differentiation in the Adult Subventricular Zone Are Not Affected by CSF1R Inhibition.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Apr 2;13:97. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00097. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31001085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohan C, Putterman C. Genetics and pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Nature Reviews: Nephrology. 2015;11:329–341. - PubMed
-
- Hanly JG. Diagnosis and management of neuropsychiatric SLE. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014;10:338–347. - PubMed
-
- Murray Peter J., Allen Judith E., Biswas Subhra K., Fisher Edward A., Gilroy Derek W., Goerdt S, Gordon S, Hamilton John A., Ivashkiv Lionel B., Lawrence T, Locati M, Mantovani A, Martinez Fernando O., Mege J-L, Mosser David M., Natoli G, Saeij Jeroen P., Schultze Joachim L., Shirey Kari A., Sica A, Suttles J, Udalova I, van Ginderachter Jo A., Vogel Stefanie N., Wynn Thomas A. Macrophage Activation and Polarization: Nomenclature and Experimental Guidelines. Immunity. 2014;41:14–20. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Orme J, Mohan C. Macrophage Subpopulations in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Discov. Med. 2012;69:151–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

