Isolation of Indole Utilizing Bacteria Arthrobacter sp. and Alcaligenes sp. From Livestock Waste
- PMID: 27570307
- PMCID: PMC4984429
- DOI: 10.1007/s12088-016-0570-z
Isolation of Indole Utilizing Bacteria Arthrobacter sp. and Alcaligenes sp. From Livestock Waste
Abstract
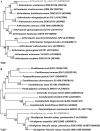
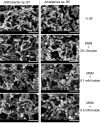
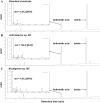
Indole is an interspecies and interkingdom signaling molecule widespread in different environmental compartment. Although multifaceted roles of indole in different biological systems have been established, little information is available on the microbial utilization of indole in the context of combating odor emissions from different types of waste. The present study was aimed at identifying novel bacteria capable of utilizing indole as the sole carbon and energy source. From the selective enrichment of swine waste and cattle feces, we identified Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria belonging to the genera Arthrobacter and Alcaligenes. Bacteria belonging to the genus Alcaligenes showed higher rates of indole utilization than Arthrobacter. Indole at 1.0 mM for growth was completely utilized by Alcaligenes sp. in 16 h. Both strains produced two intermediates, anthranilic acid and isatin, during aerobic indole metabolism. These isolates were also able to grow on several indole derivatives. Interestingly, an adaptive response in terms of a decrease in cell size was observed in both strains in the presence of indole. The present study will help to explain the degradation of indole by different bacteria and also the pathways through which it is catabolized. Furthermore, these novel bacterial isolates could be potentially useful for the in situ attenuation of odorant indole and its derivatives emitted from different types of livestock waste.
Keywords: Alcaligenes sp.; Arthrobacter sp.; Biodegradation; Environmental biotechnology; Indole.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Biodegradation of naphthalene-2-sulfonic acid present in tannery wastewater by bacterial isolates Arthrobacter sp. 2AC and Comamonas sp. 4BC.Biodegradation. 2005 Jun;16(3):237-52. doi: 10.1007/s10532-004-0889-8. Biodegradation. 2005. PMID: 15865148
-
Systematic investigation and microbial community profile of indole degradation processes in two aerobic activated sludge systems.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 11;5:17674. doi: 10.1038/srep17674. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26657581 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradation of fenoxaprop-p-ethyl by bacteria isolated from sludge.J Hazard Mater. 2005 Feb 14;118(1-3):247-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.10.020. J Hazard Mater. 2005. PMID: 15721550
-
Roles of indole as an interspecies and interkingdom signaling molecule.Trends Microbiol. 2015 Nov;23(11):707-718. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Trends Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26439294 Review.
-
[A new interspecies and interkingdom signaling molecule-Indole].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2019 Nov 25;35(11):2177-2188. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.190158. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31814363 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Biodegradation of persistent environmental pollutants by Arthrobacter sp.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Mar;26(9):8429-8443. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04358-0. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30706270
-
Indole-Induced Activities of β-Lactamase and Efflux Pump Confer Ampicillin Resistance in Pseudomonas putida KT2440.Front Microbiol. 2017 Mar 14;8:433. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00433. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28352264 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradation and Biotransformation of Indole: Advances and Perspectives.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 1;9:2625. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02625. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30443243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of an indole biodegradation gene cluster from Providencia rettgeri and its contribution in selectively biosynthesizing Tyrian purple.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jan 10;10:1109929. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1109929. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36704308 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradation characteristics and genomic analysis of a newly isolated indole-degrading strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa Jade-X.Int Microbiol. 2024 Apr;27(2):449-457. doi: 10.1007/s10123-023-00408-3. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Int Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 37490176
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
