Success of patient training in improving proficiency of eyedrop administration among various ophthalmic patient populations
- PMID: 27570445
- PMCID: PMC4986914
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S108979
Success of patient training in improving proficiency of eyedrop administration among various ophthalmic patient populations
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Success of patient training in improving proficiency of eyedrop administration among various ophthalmic patient populations [Corrigendum].Clin Ophthalmol. 2017 Feb 14;11:329. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S127289. eCollection 2017. Clin Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28243055 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the success and usefulness of patient education in eyedrop self-administration technique via an educational handout and a short instructional video.
Patients and methods: We conducted a prospective study that included 34 patients who were self-administering ophthalmic drops. Of the total patients included, 12% had used drops for <12 months, and 88% had used drops for >12 months. Average age of patients in the study was 67 years, with an age range of 19-91 years. Of the total patients included, 82% had glaucoma, 6% had dry eyes, and 12% did not have a specific diagnosis. Subjects were video recorded and assessed by a trained observer on two occasions: at baseline and after they viewed a demonstrational video and handout. A maximum score of 15 points was awarded based on 15 criteria. A written self-assessment was administered at the end of each study.
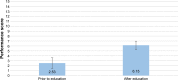
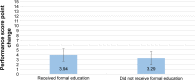
Results: Pre- and post-teaching assessment scores improved significantly with education. Patients initially scored an average 2.53 points compared to a post-education score of 6.15 out of 15 points, demonstrating a 2.43 (P=0.008) factor of improvement. After education, 94% of patients versus 47% pre-teaching (P=0.0001) pulled down their lower eyelids. A total of 91% pre-teaching versus 59% post-teaching (P=0.0042) patients squeezed one drop into the lower fornix, 74% pre-teaching versus 26% post-teaching (P=0.0002) patients released the eyelid and closed the eye for 1 minute, and 56% pre-teaching versus 3% post-teaching (P=0.0001) patients applied nasal digital pressure on each eye. We found no significant difference in score changes between those who previously received education and those who had not (P=0.37). A total of 91% patients responded in a postassessment survey that they now feel more confident of their ability to self-administer eyedrops as their doctor prescribed and that the educational materials were responsible.
Conclusion: Participants demonstrated an immediate and statistically significant improvement in several areas of proper eyedrop self-administration after exposure to a demonstration video and instructional handout.
Keywords: compliance; eye care; patient education; patient satisfaction; safety.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel Eye Drop Delivery Aid Improves Outcomes and Satisfaction.Ophthalmol Glaucoma. 2021 Sep-Oct;4(5):440-446. doi: 10.1016/j.ogla.2021.01.001. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Ophthalmol Glaucoma. 2021. PMID: 33444854
-
Patients with Low Vision Struggle with Placing Eye Drops and Benefit from an Eye Drop Aid.Ophthalmol Glaucoma. 2023 Sep-Oct;6(5):501-508. doi: 10.1016/j.ogla.2023.04.004. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Ophthalmol Glaucoma. 2023. PMID: 37084868
-
[Improved eyedrop administration and compliance in glaucoma patients. A clinical study].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1997 Oct;211(4):257-62. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1035132. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1997. PMID: 9445914 German.
-
How 'Drug Aware' are our Glaucoma Patients?J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2015 May-Aug;9(2):33-7. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10008-1181. Epub 2015 Sep 25. J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2015. PMID: 26997832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eyedrop Instillation Techniques, Difficulties, and Currently Available Solutions: A Literature Review.J Curr Ophthalmol. 2024 Mar 29;35(3):226-230. doi: 10.4103/joco.joco_308_22. eCollection 2023 Jul-Sep. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38681691 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improving eye-drop administration skills of patients - A multicenter parallel-group cluster-randomized controlled trial.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 21;14(2):e0212007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212007. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30789934 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Drop instillation and glaucoma.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2018 Mar;29(2):171-177. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000451. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29140818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of adherence between fixed and unfixed topical combination glaucoma therapies using Japanese healthcare/pharmacy claims database: a retrospective non-interventional cohort study.BMC Ophthalmol. 2021 Jan 21;21(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12886-021-01813-w. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33478408 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the effectiveness of different postoperative counseling methods for post-keratoplasty patients.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022 Feb;70(2):517-522. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1285_21. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35086229 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluating Eye Drop Instillation Technique and Its Determinants in Glaucoma Patients.J Ophthalmol. 2018 Apr 8;2018:1376020. doi: 10.1155/2018/1376020. eCollection 2018. J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29850197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaynes BI, Singa RM, Schaab G, Sorokin Y. Impact of administration angle on the cost of artificial tear solutions: does bottle positioning minimize wastage? J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2007;23:196–201. - PubMed
-
- Olthoff CM, Schouten JS, van de Borne BW, Webers CA. Noncompliance with ocular hypotensive treatment in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension: an evidence-based review. Ophthalmology. 2005;112:953–961. - PubMed
-
- Ritch R, Jamal KN, Gurses-Ozden R, Liebmann J. An improved technique of eye drop self-administration for patients with limited vision. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003;135(4):530–533. - PubMed
-
- Sleath B, Robin AL, Covert D, Byrd JE, Tudor G, Svarstad B. Patient-reported behavior and problems in using glaucoma medications. Ophthalmology. 2006;113(3):431–436. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

