Microwave-assisted green synthesis of superparamagnetic nanoparticles using fruit peel extracts: surface engineering, T 2 relaxometry, and photodynamic treatment potential
- PMID: 27570452
- PMCID: PMC4986972
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S106553
Microwave-assisted green synthesis of superparamagnetic nanoparticles using fruit peel extracts: surface engineering, T 2 relaxometry, and photodynamic treatment potential
Abstract
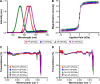
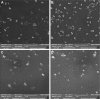
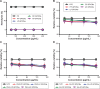
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) have the potential to be used as multimodal imaging and cancer therapy agents due to their excellent magnetism and ability to generate reactive oxygen species when exposed to light. We report the synthesis of highly biocompatible SPIONs through a facile green approach using fruit peel extracts as the biogenic reductant. This green synthesis protocol involves the stabilization of SPIONs through coordination of different phytochemicals. The SPIONs were functionalized with polyethylene glycol (PEG)-6000 and succinic acid and were extensively characterized by X-ray diffraction analysis, field emission scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, Rutherford backscattering spectrometry, diffused reflectance spectroscopy, fluorescence emission, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, and magnetization analysis. The developed SPIONs were found to be stable, almost spherical with a size range of 17-25 nm. They exhibited excellent water dispersibility, colloidal stability, and relatively high R 2 relaxivity (225 mM(-1) s(-1)). Cell viability assay data revealed that PEGylation or carboxylation appears to significantly shield the surface of the particles but does not lead to improved cytocompatibility. A highly significant increase of reactive oxygen species in light-exposed samples was found to play an important role in the photokilling of human cervical epithelial malignant carcinoma (HeLa) cells. The bio-SPIONs developed are highly favorable for various biomedical applications without risking interference from potentially toxic reagents.
Keywords: MRI contrast agent; bio synthesis; biocompatible; green approach; microwave incubation; multifunctional; photosensitive SPIONs; surface modification.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Green Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Stabilized by a Garcinia mangostana Fruit Peel Extract for Hyperthermia and Anticancer Activities.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Mar 29;16:2515-2532. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S284134. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33824589 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal and microwave synthesized SPIONs: Energy effects on the efficiency of nano drug carriers.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020 Jun;111:110792. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.110792. Epub 2020 Feb 29. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020. PMID: 32279785
-
Hypericin-bearing magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for selective drug delivery in photodynamic therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Nov 12;10:6985-96. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S92336. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 26648714 Free PMC article.
-
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for delivery of therapeutic agents: opportunities and challenges.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014 Sep;11(9):1449-70. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.924501. Epub 2014 May 29. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014. PMID: 24870351 Review.
-
Green Dentistry in Oral Cancer Treatment Using Biosynthesis Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: A Systematic Review.Cancer Manag Res. 2024 Sep 11;16:1231-1245. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S477791. eCollection 2024. Cancer Manag Res. 2024. PMID: 39282609 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioinspired Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles Based on Iron Oxides Using Orange Waste and Their Application as Photo-Activated Antibacterial Agents.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 1;24(5):4770. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054770. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902198 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle Systems for Cancer Phototherapy: An Overview.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Nov 20;11(11):3132. doi: 10.3390/nano11113132. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34835896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green synthesis and characterization of iron-oxide nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera: a potential protocol for use in low and middle income countries.BMC Res Notes. 2022 Apr 25;15(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s13104-022-06039-7. BMC Res Notes. 2022. PMID: 35468836 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-Mediated Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles with Matricaria chamomilla Aqueous Extract.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Apr 22;14(8):729. doi: 10.3390/nano14080729. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38668223 Free PMC article.
-
The In Vitro Immunomodulatory Effects Of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized From Hypoxis hemerocallidea Aqueous Extract And Hypoxoside On Macrophage And Natural Killer Cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Nov 19;14:9007-9018. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S216972. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31819415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosen JE, Chan L, Shieh D-B, Gu FX. Iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer imaging and diagnostics. Nanomedicine. 2011;8(3):275–290. - PubMed
-
- Hao H, Ma Q, He F, Yao P. Doxorubicin and Fe3O4 loaded albumin nanoparticles with folic acid modified dextran surface for tumor diagnosis and therapy. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2(45):7978–7987. - PubMed
-
- Xuan S-H, Lee S-F, Lau JT-F, et al. Photocytotoxicity and magnetic relaxivity responses of dual-porous Î3-Fe2O3@meso-SiO2 microspheres. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4(4):2033–2040. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

