Orbitally paced phosphogenesis in Mediterranean shallow marine carbonates during the middle Miocene Monterey event
- PMID: 27570497
- PMCID: PMC4984836
- DOI: 10.1002/2016GC006299
Orbitally paced phosphogenesis in Mediterranean shallow marine carbonates during the middle Miocene Monterey event
Abstract
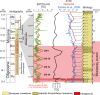
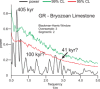
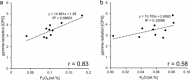
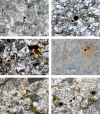
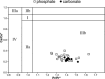
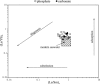
During the Oligo-Miocene, major phases of phosphogenesis occurred in the Earth's oceans. However, most phosphate deposits represent condensed or allochthonous hemipelagic deposits, formed by complex physical and chemical enrichment processes, limiting their applicability for the study regarding the temporal pacing of Miocene phosphogenesis. The Oligo-Miocene Decontra section located on the Maiella Platform (central Apennines, Italy) is a widely continuous carbonate succession deposited in a mostly middle to outer neritic setting. Of particular interest are the well-winnowed grain to packstones of the middle Miocene Bryozoan Limestone, where occurrences of authigenic phosphate grains coincide with the prominent carbon isotope excursion of the Monterey event. This unique setting allows the analysis of orbital forcing on phosphogenesis, within a bio, chemo, and cyclostratigraphically constrained age-model. LA-ICP-MS analyses revealed a significant enrichment of uranium in the studied authigenic phosphates compared to the surrounding carbonates, allowing natural gamma-radiation (GR) to be used as a qualitative proxy for autochthonous phosphate content. Time series analyses indicate a strong 405 kyr eccentricity forcing of GR in the Bryozoan Limestone. These results link maxima in the GR record and thus phosphate content to orbitally paced increases in the burial of organic carbon, particularly during the carbon isotope maxima of the Monterey event. Thus, phosphogenesis during the middle Miocene in the Mediterranean was controlled by the 405 kyr eccentricity and its influence on large-scale paleoproductivity patterns. Rare earth element data were used as a tool to reconstruct the formation conditions of the investigated phosphates, indicating generally oxic formation conditions, which are consistent with microbially mediated phosphogenesis.
Keywords: Monterey event; middle Miocene; natural gamma radiation; orbital forcing; paleoceanography; phosphogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Correlating carbon and oxygen isotope events in early to middle Miocene shallow marine carbonates in the Mediterranean region using orbitally tuned chemostratigraphy and lithostratigraphy.Paleoceanography. 2015 Apr;30(4):332-352. doi: 10.1002/2014PA002716. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Paleoceanography. 2015. PMID: 27546980 Free PMC article.
-
Correlating Mediterranean shallow water deposits with global Oligocene-Miocene stratigraphy and oceanic events.Glob Planet Change. 2013 Dec;111:226-236. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2013.09.018. Glob Planet Change. 2013. PMID: 25844021 Free PMC article.
-
Ocean Carbon Storage across the middle Miocene: a new interpretation for the Monterey Event.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 9;11(1):134. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13792-0. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 31919344 Free PMC article.
-
Global Quaternary Carbonate Burial: Proxy- and Model-Based Reconstructions and Persisting Uncertainties.Ann Rev Mar Sci. 2023 Jan 16;15:277-302. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-031122-031137. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Ann Rev Mar Sci. 2023. PMID: 35773213 Review.
-
The carbon isotope composition of ancient CO2 based on higher-plant organic matter.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2002 Apr 15;360(1793):633-58. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2001.0965. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2002. PMID: 12804297 Review.
References
-
- Abels, H. A. , Hilgen F. J., Krijgsman W., Kruk R. W., Raffi I., Turco E., and Zachariasse W. J. (2005), Long‐period orbital control on middle Miocene global cooling: Integrated stratigraphy and astronomical tuning of the Blue Clay Formation on Malta, Paleoceanography, 20, PA4012, doi:10.1029/2004PA001129. - DOI
-
- Aissaoui, D. M. , McNeil D. F., and Kirschvink J. L. (1990), Magnetostratigraphic dating of shallow‐water carbonates from Mururoa atoll, French Polynesia: Implications for global eustasy, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 97(1–2), 102–112, doi:10.1016/0012-821X(90)90102-4. - DOI
-
- Alibo, D. S. , and Nozaki Y. (1999), Rare earth elements in seawater: Particle association, shale‐normalization, and Ce oxidation, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 63(3–4), 363–372, doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00279-8. - DOI
-
- Anderson, R. F. (1982), Concentration, vertical flux, and remineralization of particulate uranium in seawater, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 46(7), 1293–1299, doi:10.1016/0016-7037(82)90013-8. - DOI
-
- Arning, E. T. , Birgel D., Brunner B., and Peckmann J. (2009), Bacterial formation of phosphatic laminites off Peru, Geobiology, 7(3), 295–307, doi:10.1111/j.1472-4669.2009.00197.x. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
