Aptamer-Mediated Transparent-Biocompatible Nanostructured Surfaces for Hepotocellular Circulating Tumor Cells Enrichment
- PMID: 27570557
- PMCID: PMC4997243
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.15284
Aptamer-Mediated Transparent-Biocompatible Nanostructured Surfaces for Hepotocellular Circulating Tumor Cells Enrichment
Abstract
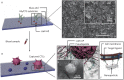
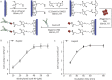
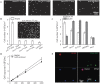
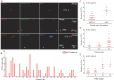
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) have been considered as the origin of cancer metastasis. Thus, detection of CTCs in peripheral blood is of great value in different types of solid tumors. However, owing to extremely low abundance of CTCs, detection of them has been technically challenging. To establish a simple and efficient method for CTCs detection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), we applied biocompatible and transparent HA/CTS (Hydroxyapatite/chitosan) nanofilm to achieve enhanced topographic interactions with nanoscale cellular surface components, and we used sLex-AP (aptamer for carbohydrate sialyl Lewis X) to coat onto HA/CTS nanofilm for efficient capture of HCC CTCs, these two functional components combined to form our CTC-(BioT)Chip platform. Using this platform, we realized HCC CTCs' capture and identification, the average recovery rate was 61.6% or more at each spiking level. Importantly, our platform identified CTCs (2±2 per 2 mL) in 25 of 42 (59.5%) HCC patients. Moreover, both the positivity rate and the number of detected CTCs were significantly correlated with tumor size, portal vein tumor thrombus, and the TNM (tumor-node-metastasis) stage. In summary, our CTC-(BioT)Chip platform provides a new method allowing for simple but efficient detection of CTCs in HCC patients, and it holds potential of clinically usefulness in monitoring HCC prognosis and guiding individualized treatment in the future.
Keywords: Aptamer; Cell capture; Circulating tumor cells; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Hydroxyapatite/chitosan.; Nanomaterial.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 2011;331:1559–64. - PubMed
-
- Gupta GP, Massague J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127:679–95. - PubMed
-
- Steeg PS. Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 2006;12:895–904. - PubMed
-
- Pantel K, Brakenhoff RH, Brandt B. Detection, clinical relevance and specific biological properties of disseminating tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:329–40. - PubMed
-
- Pantel K, Alix-Panabieres C. Circulating tumour cells in cancer patients: challenges and perspectives. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16:398–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

