Metadata-driven Clinical Data Loading into i2b2 for Clinical and Translational Science Institutes
- PMID: 27570667
- PMCID: PMC5001768
Metadata-driven Clinical Data Loading into i2b2 for Clinical and Translational Science Institutes
Abstract
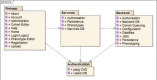
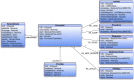
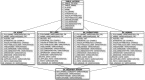
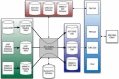
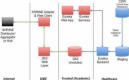
Clinical and Translational Science Award (CTSA) recipients have a need to create research data marts from their clinical data warehouses, through research data networks and the use of i2b2 and SHRINE technologies. These data marts may have different data requirements and representations, thus necessitating separate extract, transform and load (ETL) processes for populating each mart. Maintaining duplicative procedural logic for each ETL process is onerous. We have created an entirely metadata-driven ETL process that can be customized for different data marts through separate configurations, each stored in an extension of i2b2 's ontology database schema. We extended our previously reported and open source Eureka! Clinical Analytics software with this capability. The same software has created i2b2 data marts for several projects, the largest being the nascent Accrual for Clinical Trials (ACT) network, for which it has loaded over 147 million facts about 1.2 million patients.
Figures

References
-
- Committee to Review the Clinical and Translational Science Awards Program. The CTSA Program at NIH: Opportunities for Advancing Clinical and Translational Research. In: Leshner AI, Terry SF, Schultz AM, Liverman CT, editors. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US), National Academy of Sciences; 2013. - PubMed
-
- National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. CTSA Consortium Tackling Clinical Trial Recruitment Roadblocks. 2015. [updated Aug 21, 2015; cited 2015 Sep 22]; Available from: http://www.ncats.nih.gov/pubs/features/ctsa-act.
-
- Appel LJ. A primer on the design, conduct, and interpretation of clinical trials. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1(6):1360–7. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
