Adaptive anisotropic diffusion for noise reduction of phase images in Fourier domain Doppler optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 27570687
- PMCID: PMC4986803
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.7.002912
Adaptive anisotropic diffusion for noise reduction of phase images in Fourier domain Doppler optical coherence tomography
Abstract
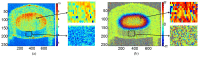
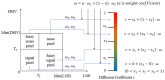
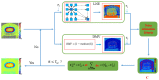
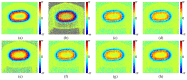
Phase image in Fourier domain Doppler optical coherence tomography offers additional flow information of investigated samples, which provides valuable evidence towards accurate medical diagnosis. High quality phase images are thus desirable. We propose a noise reduction method for phase images by combining a synthetic noise estimation criteria based on local noise estimator (LNE) and distance median value (DMV) with anisotropic diffusion model. By identifying noise and signal pixels accurately and diffusing them with different coefficients respectively and adaptive iteration steps, we demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed method in both phantom and mouse artery images. Comparison with other methods such as filtering method (mean, median filtering), wavelet method, probabilistic method and partial differential equation based methods in terms of peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), equivalent number of looks (ENL) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) showed the advantages of our method in reserving image energy and removing noise.
Keywords: (030.4280) Noise in imaging systems; (100.0100) Image processing; (110.4500) Optical coherence tomography.
Figures


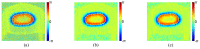

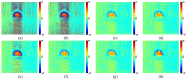

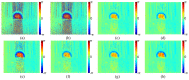


References
-
- Jia Y., Wei E., Wang X., Zhang X., Morrison J. C., Parikh M., Lombardi L. H., Gattey D. M., Armour R. L., Edmunds B., Kraus M. F., Fujimoto J. G., Huang D., “Optical coherence tomography angiography of optic disc perfusion in glaucoma,” Ophthalmology 121(7), 1322–1332 (2014).10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.01.021 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
