Data on gene and protein expression changes induced by apabetalone (RVX-208) in ex vivo treated human whole blood and primary hepatocytes
- PMID: 27570805
- PMCID: PMC4990638
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.07.047
Data on gene and protein expression changes induced by apabetalone (RVX-208) in ex vivo treated human whole blood and primary hepatocytes
Abstract
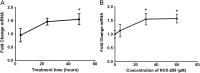
Apabetalone (RVX-208) inhibits the interaction between epigenetic regulators known as bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) proteins and acetyl-lysine marks on histone tails. Data presented here supports the manuscript published in Atherosclerosis "RVX-208, a BET-inhibitor for Treating Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease, Raises ApoA-I/HDL and Represses Pathways that Contribute to Cardiovascular Disease" (Gilham et al., 2016) [1]. It shows that RVX-208 and a comparator BET inhibitor (BETi) JQ1 increase mRNA expression and production of apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I), the main protein component of high density lipoproteins, in primary human and African green monkey hepatocytes. In addition, reported here are gene expression changes from a microarray-based analysis of human whole blood and of primary human hepatocytes treated with RVX-208.
Keywords: African green monkey; ApoA-I; Apolipoprotein A-I; BET inhibitor; BET proteins; Bromodomain; Gene expression; JQ1; Microarrays; Primary human hepatocytes; RVX-208; Vascular inflammation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RVX-208, a BET-inhibitor for treating atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, raises ApoA-I/HDL and represses pathways that contribute to cardiovascular disease.Atherosclerosis. 2016 Apr;247:48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.01.036. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Atherosclerosis. 2016. PMID: 26868508
-
Apabetalone (RVX-208) reduces vascular inflammation in vitro and in CVD patients by a BET-dependent epigenetic mechanism.Clin Epigenetics. 2019 Jul 12;11(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0696-z. Clin Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 31300040 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic BET reader inhibitor apabetalone (RVX-208) counters proinflammatory aortic gene expression in a diet induced obesity mouse model and in human endothelial cells.Atherosclerosis. 2023 Jan;364:10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.11.015. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Atherosclerosis. 2023. PMID: 36455344
-
RVX 208: A novel BET protein inhibitor, role as an inducer of apo A-I/HDL and beyond.Cardiovasc Ther. 2017 Aug;35(4). doi: 10.1111/1755-5922.12265. Cardiovasc Ther. 2017. PMID: 28423226 Review.
-
BET Epigenetic Reader Proteins in Cardiovascular Transcriptional Programs.Circ Res. 2020 Apr 24;126(9):1190-1208. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.315929. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32324495 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Benefit of Apabetalone on Plasma Proteins in Renal Disease.Kidney Int Rep. 2017 Dec 8;3(3):711-721. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2017.12.001. eCollection 2018 May. Kidney Int Rep. 2017. PMID: 29854980 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Modulation by Apabetalone Counters Cytokine-Driven Acute Phase Response In Vitro, in Mice and in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease.Cardiovasc Ther. 2020 Jul 21;2020:9397109. doi: 10.1155/2020/9397109. eCollection 2020. Cardiovasc Ther. 2020. PMID: 32821285 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Apabetalone Added to Standard Therapy on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Recent Acute Coronary Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2020 Apr 28;323(16):1565-1573. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.3308. JAMA. 2020. PMID: 32219359 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Apabetalone and hospitalization for heart failure in patients following an acute coronary syndrome: a prespecified analysis of the BETonMACE study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Jan 7;20(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01199-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33413345 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Bromodomain and Extraterminal Protein Inhibitor Apabetalone Ameliorates Kidney Injury in Diabetes by Regulating Cholesterol Accumulation and Modulating the Gut Microbiota.Kidney Int Rep. 2024 Nov 22;10(2):522-534. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.11.022. eCollection 2025 Feb. Kidney Int Rep. 2024. PMID: 39990894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gilham D. RVX-208, a BET-inhibitor for treating atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, raises ApoA-I/HDL and represses pathways that contribute to cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis. 2016;247:48–57. - PubMed
-
- Lowenstein C., Matsushita K. The acute phase response and atherosclerosis. Drug Discov. Today. 2004;1(1):17–22.
-
- Muller O. Transcriptional fingerprint of human whole blood at the site of coronary occlusion in acute myocardial infarction. EuroIntervention. 2011;7(4):458–466. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

