Isoprenoid Biosynthesis Inhibitors Targeting Bacterial Cell Growth
- PMID: 27571880
- PMCID: PMC5160999
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201600343
Isoprenoid Biosynthesis Inhibitors Targeting Bacterial Cell Growth
Abstract
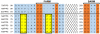
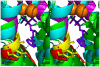
We synthesized potential inhibitors of farnesyl diphosphate synthase (FPPS), undecaprenyl diphosphate synthase (UPPS), or undecaprenyl diphosphate phosphatase (UPPP), and tested them in bacterial cell growth and enzyme inhibition assays. The most active compounds were found to be bisphosphonates with electron-withdrawing aryl-alkyl side chains which inhibited the growth of Gram-negative bacteria (Acinetobacter baumannii, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) at ∼1-4 μg mL-1 levels. They were found to be potent inhibitors of FPPS; cell growth was partially "rescued" by the addition of farnesol or overexpression of FPPS, and there was synergistic activity with known isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway inhibitors. Lipophilic hydroxyalkyl phosphonic acids inhibited UPPS and UPPP at micromolar levels; they were active (∼2-6 μg mL-1 ) against Gram-positive but not Gram-negative organisms, and again exhibited synergistic activity with cell wall biosynthesis inhibitors, but only indifferent effects with other inhibitors. The results are of interest because they describe novel inhibitors of FPPS, UPPS, and UPPP with cell growth inhibitory activities as low as ∼1-2 μg mL-1 .
Keywords: Gram-negative pathogens; Staphylococcus aureus; cell wall biosynthesis; drug discovery; membrane proteins.
© 2016 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

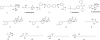
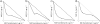
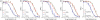
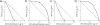
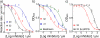

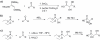
Similar articles
-
Bacterial Cell Growth Inhibitors Targeting Undecaprenyl Diphosphate Synthase and Undecaprenyl Diphosphate Phosphatase.ChemMedChem. 2016 Oct 19;11(20):2311-2319. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201600342. Epub 2016 Aug 31. ChemMedChem. 2016. PMID: 27578312 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Lipophilic Bisphosphonates That Target Bacterial Cell Wall and Quinone Biosynthesis.J Med Chem. 2019 Mar 14;62(5):2564-2581. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01878. Epub 2019 Feb 21. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30730737 Free PMC article.
-
GroEL/ES inhibitors as potential antibiotics.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Jul 1;26(13):3127-3134. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.04.089. Epub 2016 May 4. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 27184767
-
Structure- and Ligand-Dynamics-Based Design of Novel Antibiotics Targeting Lipid A Enzymes LpxC and LpxH in Gram-Negative Bacteria.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Apr 6;54(7):1623-1634. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00880. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33720682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Development of Undecaprenyl Pyrophosphate Synthase Inhibitors as Potential Antibacterials.Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(5):464-82. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666151231094854. Curr Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26718796 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization and a Kinetic Study on the Acidic Hydrolysis of Dialkyl α-Hydroxybenzylphosphonates.Molecules. 2020 Aug 20;25(17):3793. doi: 10.3390/molecules25173793. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32825450 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the antibiotic resistance mechanisms in a gram-positive and a gram-negative bacterium by gene networks analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 15;19(11):e0311434. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311434. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39546505 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphonic acid: preparation and applications.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2017 Oct 20;13:2186-2213. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.13.219. eCollection 2017. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2017. PMID: 29114326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unexpected Reaction of Dialkyl α-Hydroxy-benzylphosphonates with Dialkyl Phosphites and a Few Related Reactions.J Org Chem. 2025 Jan 10;90(1):439-447. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.4c02355. Epub 2024 Dec 17. J Org Chem. 2025. PMID: 39686731 Free PMC article.
-
Microwaves as "Co-Catalysts" or as Substitute for Catalysts in Organophosphorus Chemistry.Molecules. 2021 Feb 23;26(4):1196. doi: 10.3390/molecules26041196. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33672361 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States. Executive Summary. 2013 http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/ar-threats-2013-508.pdf.
-
- Leon A, Liu L, Yang Y, Hudock MP, Hall P, Yin F, Studer D, Puan KJ, Morita CT, Oldfield E. J. Med. Chem. 2006;49:7331–7341. - PubMed
-
- Jomaa H, Wiesner J, Sanderbrand S, Altincicek B, Weidemeyer C, Hintz M, Turbachova I, Eberl M, Zeidler J, Lichtenthaler HK, Soldati D, Beck E. Science. 1999;285:1573–1576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

