Forced co-expression of IL-21 and IL-7 in whole-cell cancer vaccines promotes antitumor immunity
- PMID: 27571893
- PMCID: PMC5004106
- DOI: 10.1038/srep32351
Forced co-expression of IL-21 and IL-7 in whole-cell cancer vaccines promotes antitumor immunity
Abstract
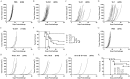
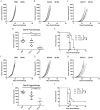
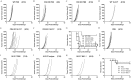
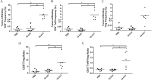
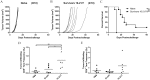
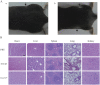
Genetic modification of whole-cell cancer vaccines to augment their efficacies has a history of over two and a half decades. Various genes and gene combinations, targeting different aspects of immune responses have been tested in pursuit of potent adjuvant effects. Here we show that co-expression of two cytokine members of the common cytokine receptor γ-chain family, IL-21 and IL-7, in whole-cell cancer vaccines boosts antitumor immunity in a CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell-dependent fashion. It also generates effective immune memory. The vaccine-elicited short-term effects positively correlated with enhanced infiltration of CD4(+) and CD8(+) effector T cells, and the long-term effects positively correlated with enhanced infiltration of effector memory T cells, especially CD8(+) effector memory T cells. Preliminary data suggested that the vaccine exhibited good safety profile in murine models. Taken together, the combination of IL-21 and IL-7 possesses potent adjuvant efficacy in whole-cell vaccines. This finding warrants future development of IL-21 and IL-7 co-expressing whole-cell cancer vaccines and their relevant combinatorial regimens.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

