Notch 2 signaling contributes to cell growth, anti-apoptosis and metastasis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 27572051
- PMCID: PMC5042778
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5688
Notch 2 signaling contributes to cell growth, anti-apoptosis and metastasis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
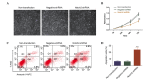
Notch signaling is important during the development of a variety of human tumors. Depending on the context, Notch signaling can be either oncogenic or anti‑proliferative, and therefore, its effects in cancer are unpredictable. The aim of the present study was to identify the importance of Notch 2 in the cell growth and metastasis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC). The current study performed quantum dots‑based immunofluorescence histochemistry to determine expression of Notch 2 in 72 LSCC samples without lymph node metastasis, 23 LSCC samples with lymph node metastasis and 31 samples from vocal cord polyps. It was observed that Notch 2 was upregulated in LSCC tissue compared with normal vocal cord polyps. This upregulation was further enhanced in LSCC tissues with lymph node metastasis compared with LSCC tissues without lymph node metastasis. Following knockdown of NOTCH2 expression in LSCC cells, the in vitro tumorigenicity of Hep‑2 cells was inhibited, with growth, migration, invasion and proliferation reduced, and apoptosis induced. Additionally, following downregulation of Notch 2 protein expression, the protein expression levels of phospho‑mitogen‑activated protein kinase 1 (p‑ERK), v‑myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog and B‑cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (Bcl2) were also downregulated, whereas, Bcl2‑associated X protein expression was upregulated. There were no changes detected in the protein expression levels of total‑ERK, phospho‑v‑akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1 (p‑Akt) and total‑Akt. The results of the present study suggest that Notch 2 is important for the cell growth, anti‑apoptosis and metastasis of LSCC. Therefore, Notch 2 inhibitors may have therapeutic potential for the treatment of patients with LSCC via the inhibition of cancer cell growth and metastasis.
Figures

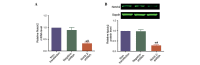


Similar articles
-
Downregulation of Notch1 induces apoptosis and inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2015 Dec;34(6):3111-9. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4274. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26398771
-
Effect of EphA7 Silencing on Proliferation, Invasion and Apoptosis in Human Laryngeal Cancer Cell Lines Hep-2 and AMC-HN-8.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(2):435-45. doi: 10.1159/000430110. Epub 2015 May 11. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25968442
-
Zinc finger protein x-linked (ZFX) contributes to patient prognosis, cell proliferation and apoptosis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Nov 1;8(11):13886-99. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26823701 Free PMC article.
-
[Cell death in malignant tumors. Relevance of cell death regulation for metastasis].Pathologe. 2015 Nov;36 Suppl 2:181-4. doi: 10.1007/s00292-015-0080-5. Pathologe. 2015. PMID: 26400565 Review. German.
-
Migrastatics: Redirecting R&D in Solid Cancer Towards Metastasis?Trends Cancer. 2019 Dec;5(12):755-756. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.10.011. Epub 2019 Nov 16. Trends Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31813449 Review.
Cited by
-
CDK5RAP2 is a Wnt target gene and promotes stemness and progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Feb 11;14(2):107. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05652-z. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 36774351 Free PMC article.
-
Overview on Molecular Biomarkers for Laryngeal Cancer: Looking for New Answers to an Old Problem.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 28;14(7):1716. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071716. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Metastasis: Focus on Laryngeal Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 1;10(9):2148. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092148. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Definition of miRNA Signatures of Nodal Metastasis in LCa: miR-449a Targets Notch Genes and Suppresses Cell Migration and Invasion.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Jun 5;20:711-724. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.04.006. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32402942 Free PMC article.
-
Notch Signaling and Human Papillomavirus-Associated Oral Tumorigenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1287:105-122. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-55031-8_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33034029 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ramdass B, Maliekal TT, Lakshmi S, Rehman M, Rema P, Nair P, Mukherjee G, Reddy BK, Krishna S, Radhakrishna Pillai M. Coexpression of Notch1 and NF kappaB signaling pathway components in human cervical cancer progression. Gynecol Oncol. 2007;104:352–361. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2006.08.054. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

