Dynamics of the human and viral m(6)A RNA methylomes during HIV-1 infection of T cells
- PMID: 27572442
- PMCID: PMC6053355
- DOI: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.11
Dynamics of the human and viral m(6)A RNA methylomes during HIV-1 infection of T cells
Abstract
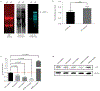
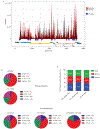
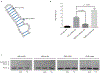
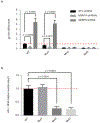
N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) is the most prevalent internal modification of eukaryotic mRNA. Very little is known of the function of m(6)A in the immune system or its role in host-pathogen interactions. Here, we investigate the topology, dynamics and bidirectional influences of the viral-host RNA methylomes during HIV-1 infection of human CD4 T cells. We show that viral infection triggers a massive increase in m(6)A in both host and viral mRNAs. In HIV-1 mRNA, we identified 14 methylation peaks in coding and noncoding regions, splicing junctions and splicing regulatory sequences. We also identified a set of 56 human gene transcripts that were uniquely methylated in HIV-1-infected T cells and were enriched for functions in viral gene expression. The functional relevance of m(6)A for viral replication was demonstrated by silencing of the m(6)A writer or the eraser enzymes, which decreased or increased HIV-1 replication, respectively. Furthermore, methylation of two conserved adenosines in the stem loop II region of HIV-1 Rev response element (RRE) RNA enhanced binding of HIV-1 Rev protein to the RRE in vivo and influenced nuclear export of RNA. Our results identify a new mechanism for the control of HIV-1 replication and its interaction with the host immune system.
Figures
Comment in
-
Viral cell biology: HIV RNA gets methylated.Nat Microbiol. 2016 Mar 29;1:16037. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.37. Nat Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27572449 No abstract available.
References
-
- Desrosiers RC, Friderici KH & Rottman FM Characterization of Novikoff hepatoma mRNA methylation and heterogeneity in the methylated 5' terminus. Biochemistry 14, 4367–4374 (1975). - PubMed
-
- Perry RP, Kelley DE, Friderici K & Rottman F The methylated constituents of L cell messenger RNA: evidence for an unusual cluster at the 5' terminus. Cell 4, 387–394 (1975). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

