p66Shc Couples Mechanical Signals to RhoA through Focal Adhesion Kinase-Dependent Recruitment of p115-RhoGEF and GEF-H1
- PMID: 27573018
- PMCID: PMC5086523
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00194-16
p66Shc Couples Mechanical Signals to RhoA through Focal Adhesion Kinase-Dependent Recruitment of p115-RhoGEF and GEF-H1
Abstract
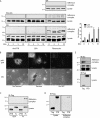
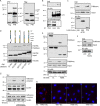
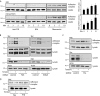
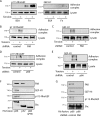
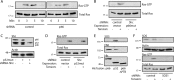
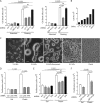
Tissue cells respond to changes in tensional forces with proliferation or death through the control of RhoA. However, the response coupling mechanisms that link force with RhoA activation are poorly understood. We found that tension applied to fibronectin-coated microbeads caused recruitment of all three isoforms of the Shc adapter (p66Shc, p52Shc, and p46Shc) to adhesion complexes. The Shc PTB domain was necessary and sufficient for this recruitment, and screening studies revealed the direct interactions with the FERM domain of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) that were required for Shc translocation to adhesion complexes. The FAK/p66Shc complex specifically bound and activated the Rho guanyl exchange factors (GEFs) p115-RhoGEF and GEF-H1, leading to tension-induced RhoA activation. In contrast, the FAK/p52Shc complex bound SOS1 but not the Rho GEFs to mediate tension-induced Ras activation. Nuclear translocation and activation of the YAP/TAZ transcription factors on firm substrates required the FAK/p66Shc/Rho GEF complex, and both proliferation on firm substrates and anoikis in suspension required signaling through p66Shc and its associated Rho GEFs. These studies reveal the binary and exclusive assignment of p66Shc and p52Shc to tension-induced Rho or Ras signals, respectively, and suggest an integrated role for the two Shc isoforms in coordinating the cellular response to mechanical stimuli.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Shc and the mechanotransduction of cellular anchorage and metastasis.Small GTPases. 2019 Jan;10(1):64-71. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1273172. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28632027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tension on JAM-A activates RhoA via GEF-H1 and p115 RhoGEF.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 May 1;27(9):1420-30. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-12-0833. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26985018 Free PMC article.
-
p66(Shc) restrains Ras hyperactivation and suppresses metastatic behavior.Oncogene. 2010 Oct 14;29(41):5559-67. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.326. Epub 2010 Aug 2. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20676142 Free PMC article.
-
The Rho GEFs LARG and GEF-H1 regulate the mechanical response to force on integrins.Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Jun;13(6):722-7. doi: 10.1038/ncb2254. Epub 2011 May 15. Nat Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21572419 Free PMC article.
-
Detachment-Based Equilibrium of Anoikic Cell Death and Autophagic Cell Survival Through Adaptor Protein p66(Shc).Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2016 Mar;299(3):325-33. doi: 10.1002/ar.23299. Epub 2015 Dec 25. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2016. PMID: 26643258
Cited by
-
Linking Extracellular Matrix Agrin to the Hippo Pathway in Liver Cancer and Beyond.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Feb 6;10(2):45. doi: 10.3390/cancers10020045. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29415512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanical microenvironment regulates ovarian cancer cell morphology, migration, and spheroid disaggregation.Sci Rep. 2018 May 8;8(1):7228. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25589-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29740072 Free PMC article.
-
Role of adaptor protein p66Shc in renal pathologies.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Feb 1;314(2):F143-F153. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00414.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28978535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p66ShcA promotes malignant breast cancer phenotypes by alleviating energetic and oxidative stress.Redox Biol. 2024 Apr;70:103028. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103028. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38211442 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Redox Enzyme p66Shc in Biological Aging of the Lung.Aging Dis. 2024 Apr 1;15(2):911-926. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0715. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 37548932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harden N, Ricos M, Ong YM, Chia W, Lim L. 1999. Participation of small GTPases in dorsal closure of the Drosophila embryo: distinct roles for Rho subfamily proteins in epithelial morphogenesis. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 3):273–284. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
