Dopaminergic inputs in the dentate gyrus direct the choice of memory encoding
- PMID: 27573822
- PMCID: PMC5027420
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1606951113
Dopaminergic inputs in the dentate gyrus direct the choice of memory encoding
Abstract
Rewarding experiences are often well remembered, and such memory formation is known to be dependent on dopamine modulation of the neural substrates engaged in learning and memory; however, it is unknown how and where in the brain dopamine signals bias episodic memory toward preceding rather than subsequent events. Here we found that photostimulation of channelrhodopsin-2-expressing dopaminergic fibers in the dentate gyrus induced a long-term depression of cortical inputs, diminished theta oscillations, and impaired subsequent contextual learning. Computational modeling based on this dopamine modulation indicated an asymmetric association of events occurring before and after reward in memory tasks. In subsequent behavioral experiments, preexposure to a natural reward suppressed hippocampus-dependent memory formation, with an effective time window consistent with the duration of dopamine-induced changes of dentate activity. Overall, our results suggest a mechanism by which dopamine enables the hippocampus to encode memory with reduced interference from subsequent experience.
Keywords: channelrhodopsin-2; dopamine; temporal difference learning; theta oscillation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
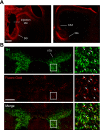
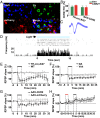
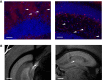



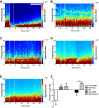
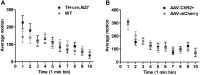

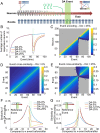
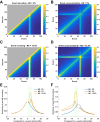
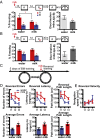




References
-
- Shohamy D, Adcock RA. Dopamine and adaptive memory. Trends Cogn Sci. 2010;14(10):464–472. - PubMed
-
- Wise RA. Dopamine, learning and motivation. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5(6):483–494. - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Chan VT, Merzenich MM. Cortical remodelling induced by activity of ventral tegmental dopamine neurons. Nature. 2001;412(6842):79–83. - PubMed
-
- Burgess N, Maguire EA, O’Keefe J. The human hippocampus and spatial and episodic memory. Neuron. 2002;35(4):625–641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

