IL2Rβ-dependent signals drive terminal exhaustion and suppress memory development during chronic viral infection
- PMID: 27573835
- PMCID: PMC5027416
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1604256113
IL2Rβ-dependent signals drive terminal exhaustion and suppress memory development during chronic viral infection
Abstract
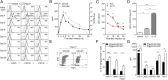
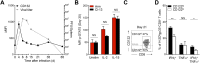
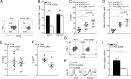
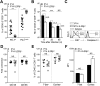
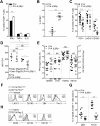
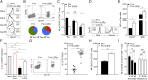
Exhaustion of CD8(+) T cells severely impedes the adaptive immune response to chronic viral infections. Despite major advances in our understanding of the molecular regulation of exhaustion, the cytokines that directly control this process during chronicity remain unknown. We demonstrate a direct impact of IL-2 and IL-15, two common gamma-chain-dependent cytokines, on CD8(+) T-cell exhaustion. Common to both cytokine receptors, the IL-2 receptor β (IL2Rβ) chain is selectively maintained on CD8(+) T cells during chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus and hepatitis C virus infections. Its expression correlates with exhaustion severity and identifies terminally exhausted CD8(+) T cells both in mice and humans. Genetic ablation of the IL2Rβ chain on CD8(+) T cells restrains inhibitory receptor induction, in particular 2B4 and Tim-3; precludes terminal differentiation of highly defective PD-1(hi) effectors; and rescues memory T-cell development and responsiveness to IL-7-dependent signals. Together, we ascribe a previously unexpected role to IL-2 and IL-15 as instigators of CD8(+) T-cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection.
Keywords: CD8 T cell; IL-15; IL-2; exhaustion; memory T cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


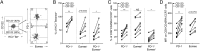

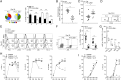
Similar articles
-
Cooperation of Tim-3 and PD-1 in CD8 T-cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 17;107(33):14733-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009731107. Epub 2010 Aug 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20679213 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Memory and Exhaustion: Clinically Relevant Lessons from the LCMV Model.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;850:137-52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-15774-0_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26324351 Review.
-
IRF9 Prevents CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion in an Extrinsic Manner during Acute Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Infection.J Virol. 2017 Oct 27;91(22):e01219-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01219-17. Print 2017 Nov 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28878077 Free PMC article.
-
On the role of the inhibitory receptor LAG-3 in acute and chronic LCMV infection.Int Immunol. 2010 Jan;22(1):13-23. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxp107. Epub 2009 Oct 30. Int Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19880580
-
CD8 T cell dysfunction during chronic viral infection.Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Aug;19(4):408-15. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.06.004. Epub 2007 Jul 25. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17656078 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-15 promotes self-renewal of progenitor exhausted CD8 T cells during persistent antigenic stimulation.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 20;14:1117092. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1117092. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37409128 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Modeling of CD8 T Cell Exhaustion Enables CRISPR Screening to Reveal a Role for BHLHE40.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 17:2023.04.17.537229. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.17.537229. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Sci Immunol. 2023 Aug 25;8(86):eade3369. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.ade3369. PMID: 37131713 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A glimpse into the application of the immunomodulatory effect of IL-2 in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 23;12:1552473. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1552473. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40337274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An engineered immunocytokine with collagen affinity improves the tumor bioavailability, tolerability, and therapeutic efficacy of IL-2.Cell Rep Med. 2023 Nov 21;4(11):101289. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101289. Cell Rep Med. 2023. PMID: 37992685 Free PMC article.
-
'Stem-like' precursors are the fount to sustain persistent CD8+ T cell responses.Nat Immunol. 2022 Jun;23(6):836-847. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01219-w. Epub 2022 May 27. Nat Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35624209 Review.
References
-
- Zehn D, Wherry EJ. Immune memory and exhaustion: Clinically relevant lessons from the LCMV model. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;850:137–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

