Genistein targets the cancerous inhibitor of PP2A to induce growth inhibition and apoptosis in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 27574003
- PMCID: PMC4948957
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3588
Genistein targets the cancerous inhibitor of PP2A to induce growth inhibition and apoptosis in breast cancer cells
Abstract
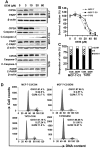
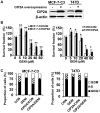
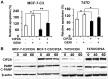
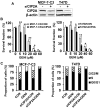
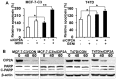
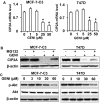
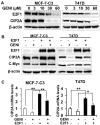
Genistein is a soy isoflavone with phytoestrogen and tyrosine kinase inhibitory properties. High intake of soy/genistein has been associated with reduced breast cancer risk. Despite the advances in genistein-mediated antitumor studies, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. In the present study, we investigated genistein-induced regulation of the cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (CIP2A), a novel oncogene frequently overexpressed in breast cancer, and its functional impact on genistein-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis. We demonstrated that genistein induced downregulation of CIP2A in MCF-7-C3 and T47D breast cancer cells, which was correlated with its growth inhibition and apoptotic activities. Overexpression of CIP2A attenuated, whereas CIP2A knockdown sensitized, genistein-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis. We further showed that genistein-induced downregulation of CIP2A involved both transcriptional suppression and proteasomal degradation. In particular, genistein at higher concentrations induced concurrent downregulation of E2F1 and CIP2A. Overexpression of E2F1 attenuated genistein-induced downregulation of CIP2A mRNA, indicating the role of E2F1 in genistein-induced transcriptional suppression of CIP2A. Taken together, our results identified CIP2A as a functional target of genistein and demonstrated that modulation of E2F1-mediated transcriptional regulation of CIP2A contributes to its downregulation. These data advance our understanding of genistein-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis, and support further investigation on CIP2A as a therapeutic target of relevant anticancer agents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Senescence sensitivity of breast cancer cells is defined by positive feedback loop between CIP2A and E2F1.Cancer Discov. 2013 Feb;3(2):182-97. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0292. Epub 2013 Jan 10. Cancer Discov. 2013. PMID: 23306062 Free PMC article.
-
Tamoxifen induces apoptosis through cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A-dependent phospho-Akt inactivation in estrogen receptor-negative human breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Sep 17;16(5):431. doi: 10.1186/s13058-014-0431-9. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25228280 Free PMC article.
-
CIP2A is a target of bortezomib in human triple negative breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Apr 26;14(2):R68. doi: 10.1186/bcr3175. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22537901 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic nexus of cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (CIP2A): an oncoprotein with many hands.Oncotarget. 2014 Jul 15;5(13):4581-602. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2127. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25015035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A, an emerging human oncoprotein and a potential cancer therapy target.Cancer Res. 2013 Nov 15;73(22):6548-53. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1994. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24204027 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive nutraceuticals as G4 stabilizers: potential cancer prevention and therapy-a critical review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Jun;397(6):3585-3616. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02857-z. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38019298 Review.
-
The Role of Genistein and its Derivatives in Ovarian Cancer: New Perspectives for Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(5):907-922. doi: 10.2174/0109298673251713231019091910. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 37921172 Review.
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Modulated by Genistein in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 27;26(3):1114. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031114. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caesalpinia pulcherrima lowered serum carcinoembryonic antigen and antigen 125 in 7,12-Dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced Mammary Carcinogenesis in Female Albino Rats.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 5;10(1):e23401. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23401. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38187255 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Effects of Combining Genistein with Aromatase Inhibitors: Concerns Regarding Its Consumption during Breast Cancer Treatment.Molecules. 2023 Jun 21;28(13):4893. doi: 10.3390/molecules28134893. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nagata C, Mizoue T, Tanaka K, Tsuji I, Tamakoshi A, Matsuo K, Wakai K, Inoue M, Tsugane S, Sasazuki S, et al. Research Group for the Development and Evaluation of Cancer Prevention Strategies in Japan: Soy intake and breast cancer risk: An evaluation based on a systematic review of epidemiologic evidence among the Japanese population. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014;44:282–295. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyt203. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lamartiniere CA. Protection against breast cancer with genistein: a component of soy. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;71:1705S–1707S. discussion 1708S–1709S. - PubMed
-
- Shao ZM, Shen ZZ, Fontana JA, Barsky SH. Genistein’s ‘ER-dependent and independent’ actions are mediated through ER pathways in ER-positive breast carcinoma cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2000;20:2409–2416. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

