The roadmap for estimation of cell-type-specific neuronal activity from non-invasive measurements
- PMID: 27574309
- PMCID: PMC5003857
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0356
The roadmap for estimation of cell-type-specific neuronal activity from non-invasive measurements
Abstract
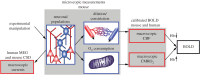
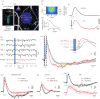
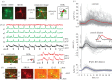
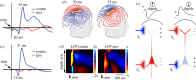
The computational properties of the human brain arise from an intricate interplay between billions of neurons connected in complex networks. However, our ability to study these networks in healthy human brain is limited by the necessity to use non-invasive technologies. This is in contrast to animal models where a rich, detailed view of cellular-level brain function with cell-type-specific molecular identity has become available due to recent advances in microscopic optical imaging and genetics. Thus, a central challenge facing neuroscience today is leveraging these mechanistic insights from animal studies to accurately draw physiological inferences from non-invasive signals in humans. On the essential path towards this goal is the development of a detailed 'bottom-up' forward model bridging neuronal activity at the level of cell-type-specific populations to non-invasive imaging signals. The general idea is that specific neuronal cell types have identifiable signatures in the way they drive changes in cerebral blood flow, cerebral metabolic rate of O2 (measurable with quantitative functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging), and electrical currents/potentials (measurable with magneto/electroencephalography). This forward model would then provide the 'ground truth' for the development of new tools for tackling the inverse problem-estimation of neuronal activity from multimodal non-invasive imaging data.This article is part of the themed issue 'Interpreting BOLD: a dialogue between cognitive and cellular neuroscience'.
Keywords: BOLD fMRI; CMRO2; cerebral blood flow; magnetoencephalography; neurometabolic; neurovascular.
© 2016 The Author(s).
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DP1 OD006831/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R24 NS092986/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR029050/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000790/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057198/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS091230/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA029706/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB003832/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS055104/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036722/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH111359/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG042026/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 NS082097/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

