Effects of roflumilast in COPD patients receiving inhaled corticosteroid/long-acting β2-agonist fixed-dose combination: RE(2)SPOND rationale and study design
- PMID: 27574416
- PMCID: PMC4994799
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S109661
Effects of roflumilast in COPD patients receiving inhaled corticosteroid/long-acting β2-agonist fixed-dose combination: RE(2)SPOND rationale and study design
Abstract
Background: Roflumilast, a once-daily, selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, reduces the risk of COPD exacerbations in patients with severe COPD associated with chronic bronchitis and a history of exacerbations. The RE(2)SPOND study is examining whether roflumilast, when added to an inhaled corticosteroid/long-acting β2-agonist (ICS/LABA) fixed-dose combination (FDC), further reduces exacerbations. The methodology is described herein.
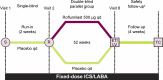
Methods: In this Phase IV, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial, participants were randomized 1:1 (stratified by long-acting muscarinic antagonist use) to receive roflumilast or placebo, plus ICS/LABA FDC, for 52 weeks. Eligible participants had severe COPD associated with chronic bronchitis, had two or more moderate-severe exacerbations within 12 months, and were receiving ICS/LABA FDC for ≥3 months. The primary efficacy measure is the rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations per participant per year. The secondary efficacy outcomes include mean change in prebronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) over 52 weeks, rate of severe exacerbations, and rate of moderate, severe, or antibiotic-treated exacerbations. Additional assessments include spirometry, rescue medication use, the COPD assessment test, daily symptoms using the EXACT-Respiratory symptoms (E-RS) questionnaire, all-cause and COPD-related hospitalizations, and safety and pharmacokinetic measures.
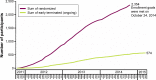
Results: Across 17 countries, 2,354 participants were randomized from September 2011 to October 2014. Enrollment goal was met in October 2014, and study completion occurred in June 2016.
Conclusion: This study will further characterize the effects of roflumilast added to ICS/LABA on exacerbation rates, lung function, and health of severe-very severe COPD participants at risk of further exacerbations. The results will determine the clinical benefits of roflumilast combined with standard-of-care inhaled COPD treatment.
Keywords: ICS/LABA; RE2SPOND; exacerbation; methodology; phosphodiesterase-4; study design.
Figures
References
-
- Tashkin DP. Roflumilast: the new orally active, selective phophodiesterase-4 inhibitor, for the treatment of COPD. Expert Opin Pharma-cother. 2014;15(1):85–96. - PubMed
-
- Hatzelmann A, Morcillo EJ, Lungarella G, et al. The preclinical pharmacology of roflumilast – a selective, oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor in development for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010;23(4):235–256. - PubMed
-
- Heron M. Deaths: Leading Causes for 2010. National Vital Statistics Reports. 6. Vol. 62. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2013. - PubMed
-
- Ford ES, Murphy LB, Khavjou O, Giles WH, Holt JB, Croft JB. Total and state-specific medical and absenteeism costs of COPD among adults aged ≥ 18 years in the United States for 2010 and projections through 2020. Chest. 2015;147(1):31–45. - PubMed
-
- Wouters EF, Groenewegen KH, Dentener MA, Vernooy JH. Systemic inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the role of exacerbations. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2007;4(8):626–634. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

