The Anti-apoptotic Effect of Ghrelin on Restraint Stress-Induced Thymus Atrophy in Mice
- PMID: 27574503
- PMCID: PMC5002450
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2016.16.4.242
The Anti-apoptotic Effect of Ghrelin on Restraint Stress-Induced Thymus Atrophy in Mice
Abstract
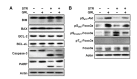
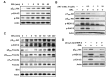
Thymic atrophy is a complication that results from exposure to many environmental stressors, disease treatments, and microbial challenges. Such acute stress-associated thymic loss can have a dramatic impact on the host's ability to replenish the necessary naïve T cell output to reconstitute the peripheral T cell numbers and repertoire to respond to new antigenic challenges. We have previously reported that treatment with the orexigenic hormone ghrelin results in an increase in the number and proliferation of thymocytes after dexamethasone challenge, suggesting a role for ghrelin in restraint stress-induced thymic involution and cell apoptosis and its potential use as a thymostimulatory agent. In an effort to understand how ghrelin suppresses thymic T cell apoptosis, we have examined the various signaling pathways induced by receptor-specific ghrelin stimulation using a restraint stress mouse model. In this model, stress-induced apoptosis in thymocytes was effectively blocked by ghrelin. Western blot analysis demonstrated that ghrelin prevents the cleavage of pro-apoptotic proteins such as Bim, Caspase-3, and PARP. In addition, ghrelin stimulation activates the Akt and Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling pathways in a time/dose-dependent manner. Moreover, we also revealed the involvement of the FoxO3a pathway in the phosphorylation of Akt and ERK1/2. Together, these findings suggest that ghrelin inhibits apoptosis by modulating the stress-induced apoptotic signal pathway in the restraint-induced thymic apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Ghrelin; Restraint stress; Thymic atrophy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ghrelin augments murine T-cell proliferation by activation of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, extracellular signal-regulated kinase and protein kinase C signaling pathways.FEBS Lett. 2014 Dec 20;588(24):4708-19. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.10.044. Epub 2014 Nov 18. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 25447526 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta and ERK1/2 pathways mediate protective effects of acylated and unacylated ghrelin against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced apoptosis in primary rat cortical neuronal cells.J Endocrinol. 2008 Sep;198(3):511-21. doi: 10.1677/JOE-08-0160. Epub 2008 Jun 9. J Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18541646
-
Ghrelin promotes thymopoiesis during aging.J Clin Invest. 2007 Oct;117(10):2778-90. doi: 10.1172/JCI30248. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17823656 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines, leptin, and stress-induced thymic atrophy.J Leukoc Biol. 2008 Oct;84(4):915-23. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0108025. Epub 2008 May 21. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 18495786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ghrelin protects against depleted uranium-induced apoptosis of MC3T3-E1 cells through oxidative stress-mediated p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 Jan 1;290:116-25. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.10.022. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26529667
Cited by
-
Effects of ghrelin supplementation on the acute phase of Chagas disease in rats.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Nov 9;12(1):532. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3787-y. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31706334 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressant-like Effects of Combined Fluoxetine and Zinc Treatment in Mice Exposed to Chronic Restraint Stress Are Related to Modulation of Histone Deacetylase.Molecules. 2021 Dec 21;27(1):22. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010022. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011254 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Effect of Ghrelin on Body Systems.Int J Endocrinol. 2020 May 25;2020:1385138. doi: 10.1155/2020/1385138. eCollection 2020. Int J Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32565790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrathymic somatotropic circuitry: consequences upon thymus involution.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 22;14:1108630. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1108630. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37426675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymus Degeneration in Women and the Influence of Female Sexual Hormones on Thymic Epithelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 26;26(7):3014. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073014. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243626 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

