Application of Bayesian Approach to Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Antiviral Treatments in Chronic Hepatitis B
- PMID: 27574976
- PMCID: PMC5004843
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161936
Application of Bayesian Approach to Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Antiviral Treatments in Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a major problem for public health; timely antiviral treatment can significantly prevent the progression of liver damage from HBV by slowing down or stopping the virus from reproducing. In the study we applied Bayesian approach to cost-effectiveness analysis, using Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulation methods for the relevant evidence input into the model to evaluate cost-effectiveness of entecavir (ETV) and lamivudine (LVD) therapy for chronic hepatitis B (CHB) in Jiangsu, China, thus providing information to the public health system in the CHB therapy.
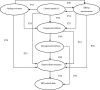
Methods: Eight-stage Markov model was developed, a hypothetical cohort of 35-year-old HBeAg-positive patients with CHB was entered into the model. Treatment regimens were LVD100mg daily and ETV 0.5 mg daily. The transition parameters were derived either from systematic reviews of the literature or from previous economic studies. The outcome measures were life-years, quality-adjusted lifeyears (QALYs), and expected costs associated with the treatments and disease progression. For the Bayesian models all the analysis was implemented by using WinBUGS version 1.4.
Results: Expected cost, life expectancy, QALYs decreased with age. Cost-effectiveness increased with age. Expected cost of ETV was less than LVD, while life expectancy and QALYs were higher than that of LVD, ETV strategy was more cost-effective. Costs and benefits of the Monte Carlo simulation were very close to the results of exact form among the group, but standard deviation of each group indicated there was a big difference between individual patients.
Conclusions: Compared with lamivudine, entecavir is the more cost-effective option. CHB patients should accept antiviral treatment as soon as possible as the lower age the more cost-effective. Monte Carlo simulation obtained costs and effectiveness distribution, indicate our Markov model is of good robustness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of nucleoside analog therapy for hepatitis B in China: a Markov analysis.Value Health. 2010 Aug;13(5):592-600. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2010.00733.x. Epub 2010 Apr 30. Value Health. 2010. PMID: 20561341
-
Economic implications of entecavir treatment in suppressing viral replication in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients in China from a perspective of the Chinese Social Security program.Value Health. 2008 Mar;11 Suppl 1:S11-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2008.00362.x. Value Health. 2008. PMID: 18387054
-
Economic analysis between entecavir and lamivudine for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in Hong Kong.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Jul;27(7):1167-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.07047.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22141402
-
Entecavir for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection.Health Technol Assess. 2009 Oct;13 Suppl 3:31-6. doi: 10.3310/hta13suppl3/05. Health Technol Assess. 2009. PMID: 19846026 Review.
-
Evaluating anti-viral drug selection and treatment duration in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B: a cost-effectiveness analysis.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008 Jun;27(12):1240-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03691.x. Epub 2008 Mar 27. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18373637 Review.
Cited by
-
Are Published Health Economic Models for Chronic Hepatitis B Appropriately Capturing the Benefits of HBsAg Loss? A Systematic Literature Review.Pharmacoecon Open. 2020 Sep;4(3):403-418. doi: 10.1007/s41669-019-00175-w. Pharmacoecon Open. 2020. PMID: 31428938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparing Efficacy of Lamivudine, Adefovir Dipivoxil, Telbivudine, and Entecavir in Treating Nucleoside Analogues Naïve for HBeAg-Negative Hepatitis B with Medium Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA Levels.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Nov 2;23:5230-5236. doi: 10.12659/msm.903382. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 29095799 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian Regression Model for a Cost-Utility and Cost-Effectiveness Analysis Comparing Punch Grafting Versus Usual Care for the Treatment of Chronic Wounds.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 May 28;17(11):3823. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17113823. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32481604 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with disease progression and viral replication in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Jun;17(6):4730-4740. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7482. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31086607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yuan Y, IIoeje U, Li H, Hay J, Yao GB. Economic implications of entecavir treatment in suppressing viral replication in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients in China from a perspective of the Chinese Social Security program. Value Health. 2008;11:S11–22. 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2008.00362.x . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Palumbo E. Lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B: a brief review. Braz J Infect Dis 2008;12(5):355–7.. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources