Oxidative Stress Facilitates IFN-γ-Induced Mimic Extracellular Trap Cell Death in A549 Lung Epithelial Cancer Cells
- PMID: 27575372
- PMCID: PMC5004888
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162157
Oxidative Stress Facilitates IFN-γ-Induced Mimic Extracellular Trap Cell Death in A549 Lung Epithelial Cancer Cells
Abstract
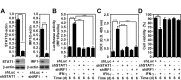
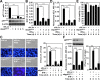
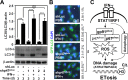
We previously demonstrated that IFN-γ induces an autophagy-regulated mimic extracellular trap cell death (ETosis) in A549 human lung cancer cells. Regarding reactive oxygen species (ROS) are involved in ETosis, this study investigated the role of oxidative stress. After IFN-γ stimulation, a necrosis-like cell death mimic ETosis occurred accompanied by the inhibition of cell growth, aberrant nuclear staining, and nucleosome release. ROS were generated in a time-dependent manner with an increase in NADPH oxidase component protein expression. STAT1-mediated IFN regulatory factor-1 activation was essential for upregulating ROS production. By genetically silencing p47phox, IFN-γ-induced ROS and mimic ETosis were significantly attenuated. This mechanistic study indicated that ROS may mediate DNA damage followed by histone H3 citrullination. Furthermore, ROS promoted IFN-γ-induced mimic ETosis in cooperation with autophagy. These findings further demonstrate that ROS regulates IFN-γ-induced mimic ETosis in lung epithelial malignancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

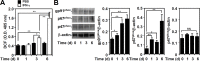

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

