Development of a rapid phenotypic test for HCV protease inhibitors with potential use in clinical decisions
- PMID: 27575432
- PMCID: PMC5004841
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2016-0022
Development of a rapid phenotypic test for HCV protease inhibitors with potential use in clinical decisions
Abstract
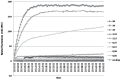
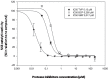
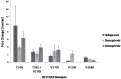
Approximately 185 million people worldwide are chronically infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV). The first-wave of approved NS3 protease inhibitors (PIs) were Telaprevir and Boceprevir, which are currently discontinued. Simeprevir is a second-wave PI incorporated into the Brazilian hepatitis C treatment protocol. Drug resistance plays a key role in patients' treatment regimen. Here, we developed a simple phenotypic assay to evaluate the impact of resistance mutations in HCV NS3 protease to PIs, using a protein expression vector containing wild type NS3 protease domain and NS4A co-factor. We analyzed the impact of five resistance mutations (T54A, V36M, V158I, V170I and T54S+V170I) against Telaprevir, Boceprevir and Simeprevir. Protein purifications were performed with low cost methodology, and enzymatic inhibition assays were measured by FRET. We obtained recombinant proteases with detectable activity, and IC50 and fold change values for the evaluated PIs were determined. The variant T54A showed the highest reduction of susceptibility for the PIs, while the other four variants exhibited lower levels of reduced susceptibility. Interestingly, V170I showed 3.2-fold change for Simeprevir, a new evidence about this variant. These results emphasize the importance of enzymatic assays in phenotypic tests to determine which therapeutic regimen should be implemented.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HCV genotype 1-6 NS3 residue 80 substitutions impact protease inhibitor activity and promote viral escape.J Hepatol. 2019 Mar;70(3):388-397. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.10.031. Epub 2018 Nov 3. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30395912
-
Hepatitis C virus NS3 protease genotyping and drug concentration determination during triple therapy with telaprevir or boceprevir for chronic infection with genotype 1 viruses, southeastern France.J Med Virol. 2014 Nov;86(11):1868-76. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24016. Epub 2014 Jul 23. J Med Virol. 2014. PMID: 25052594
-
Characterization of resistance to the protease inhibitor boceprevir in hepatitis C virus-infected patients.Hepatology. 2009 Dec;50(6):1709-18. doi: 10.1002/hep.23192. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19787809 Clinical Trial.
-
NS3 protease polymorphisms and genetic barrier to drug resistance of distinct hepatitis C virus genotypes from worldwide treatment-naïve subjects.J Viral Hepat. 2016 Nov;23(11):840-849. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12503. Epub 2016 Jan 18. J Viral Hepat. 2016. PMID: 26775769 Review.
-
[Telaprevir resistance].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2013 Jul;31 Suppl 3:26-32. doi: 10.1016/S0213-005X(13)70121-6. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2013. PMID: 24063900 Review. Spanish.
References
-
- Abrahim-Vieira B, da Costa ECB, Azevedo PHR de A, Portela AC, Dias LRS, Pinheiro S, Tanuri A, Capaccia AM, Ventura GT, Mohana-Borges R, et al. Novel isomannide-based peptide mimetics containing a tartaric acid backbone as serine protease inhibitors. Med Chem Res. 2014;23:5305–5320.
-
- Bartenschlager R, Lohmann V, Penin F. The molecular and structural basis of advanced antiviral therapy for hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11:482–496. - PubMed
-
- Binder J, Tetangco S, Weinshank M, Maegley K, Lingardo L, Diehl W, Love R, Patick AK, Smith GJ., 3rd Development of hepatitis C virus chimeric replicons for identifying broad spectrum NS3 protease inhibitors. Antiviral Res. 2011;91:102–111. - PubMed
-
- De Clercq E. Current race in the development of DAAs (direct-acting antivirals) against HCV. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;89:441–452. - PubMed
-
- Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Gonçales FL, Jr, Häussinger D, Diago M, Carosi G, Dhumeaux D, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:975–982. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

