The Rational Design, Synthesis, and Antimicrobial Properties of Thiophene Derivatives That Inhibit Bacterial Histidine Kinases
- PMID: 27575438
- PMCID: PMC5957078
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00580
The Rational Design, Synthesis, and Antimicrobial Properties of Thiophene Derivatives That Inhibit Bacterial Histidine Kinases
Abstract
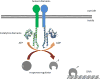
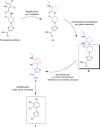
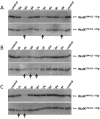
The emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria emphasizes the urgent need for novel antibacterial compounds targeting unique cellular processes. Two-component signal transduction systems (TCSs) are commonly used by bacteria to couple environmental stimuli to adaptive responses, are absent in mammals, and are embedded in various pathogenic pathways. To attenuate these signaling pathways, we aimed to target the TCS signal transducer histidine kinase (HK) by focusing on their highly conserved adenosine triphosphate-binding domain. We used a structure-based drug design strategy that begins from an inhibitor-bound crystal structure and includes a significant number of structurally simplifiying "intuitive" modifications to arrive at the simple achiral, biaryl target structures. Thus, ligands were designed, leading to a series of thiophene derivatives. These compounds were synthesized and evaluated in vitro against bacterial HKs. We identified eight compounds with significant inhibitory activities against these proteins, two of which exhibited broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. The compounds were also evaluated as adjuvants for the treatment of resistant bacteria. One compound was found to restore the sensivity of these bacteria to the respective antibiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Repurposing Hsp90 inhibitors as antibiotics targeting histidine kinases.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017 Dec 1;27(23):5235-5244. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.10.036. Epub 2017 Oct 19. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017. PMID: 29110989
-
Bacterial histidine kinases as novel antibacterial drug targets.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Jan 16;10(1):213-24. doi: 10.1021/cb5007135. Epub 2014 Dec 26. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25436989 Review.
-
Repurposing Hsp90 inhibitors as antimicrobials targeting two-component systems identifies compounds leading to loss of bacterial membrane integrity.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Aug 6;12(8):e0014624. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00146-24. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38917423 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-activity relationships of new cyanothiophene inhibitors of the essential peptidoglycan biosynthesis enzyme MurF.Eur J Med Chem. 2013 Aug;66:32-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.05.013. Epub 2013 May 21. Eur J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23786712
-
Histidine kinases as targets for new antimicrobial agents.Bioorg Med Chem. 2002 Apr;10(4):855-67. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(01)00355-8. Bioorg Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 11836091 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Thiazolylketenyl Quinazolinones as Potential Anti-MRSA Agents and Allosteric Modulator for PBP2a.Molecules. 2023 May 22;28(10):4240. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104240. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241983 Free PMC article.
-
Drug repositioning: doxazosin attenuates the virulence factors and biofilm formation in Gram-negative bacteria.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jun;107(11):3763-3778. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12522-3. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37079062
-
Synthesis of histidine kinase inhibitors and their biological properties.Med Res Rev. 2020 Jul;40(4):1440-1495. doi: 10.1002/med.21651. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Med Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 31802520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance: Two-Component Regulatory Systems and Multidrug Efflux Pumps.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 May 26;12(6):965. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12060965. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rational Design of Selective Adenine-Based Scaffolds for Inactivation of Bacterial Histidine Kinases.J Med Chem. 2017 Oct 12;60(19):8170-8182. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01066. Epub 2017 Oct 3. J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28933546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kumarasamy KK, Toleman MA, Walsh TR, Bagaria J, Butt F, Balakrishnan R, Chaudhary U, Doumith M, Giske CG, Irfan S, Krishnan P, Kumar AV, Maharjan S, Mushtaq S, Noorie T, Paterson DL, Pearson A, Perry C, Pike R, Rao B, Ray U, Sarma JB, Sharma M, Sheridan E, Thirunarayan MA, Turton J, Upadhyay S, Warner M, Welfare W, Livermore DM, Woodford N. Emergenceof a New Antibiotic Resistance Mechanism in India, Pakistan, and the UK: A Molecular, Biological, and Epidemiological Study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2010;10(9):597–602. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deurenberg RH, Stobberingh EE. TheMolecular Evolution of Hospital- and Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Curr Mol Med. 2009;9(2):100–115. - PubMed
-
- de Kraker MEA, Wolkewitz M, Davey PG, Koller W, Berger J, Nagler J, Icket C, Kalenic S, Horvatic J, Seifert H, Kaasch AJ, Paniara O, Argyropoulou A, Bompola M, Smyth E, Skally M, Raglio A, Dumpis U, Kelmere AM, Borg M, Xuereb D, Ghita MC, Noble M, Kolman J, Grabljevec S, Turner D, Lansbury L, Grundmann H, BURDEN Study Group Clinical Impact of Antimicrobial Resistance in European Hospitals: Excess Mortality and Length of Hospital Stay Related to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Bloodstream Infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55(4):1598–1605. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Walsh C. Molecular Mechanisms That Confer Antibacterial Drug Resistance. Nature. 2000;406(6797):775–781. - PubMed
-
- Levings RS, Lightfoot D, Partridge SR, Hall RM, Djordjevic SP. TheGenomic Island SGI1, Containing the Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Region of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium DT104 or Variants of It, Is Widely Distributed in Other S. Enterica Serovars. J Bacteriol. 2005;187(13):4401–4409. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

