SNP-markers in Allium species to facilitate introgression breeding in onion
- PMID: 27576474
- PMCID: PMC5006257
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-016-0879-0
SNP-markers in Allium species to facilitate introgression breeding in onion
Abstract
Background: Within onion, Allium cepa L., the availability of disease resistance is limited. The identification of sources of resistance in related species, such as Allium roylei and Allium fistulosum, was a first step towards the improvement of onion cultivars by breeding. SNP markers linked to resistance and polymorphic between these related species and onion cultivars are a valuable tool to efficiently introgress disease resistance genes. In this paper we describe the identification and validation of SNP markers valuable for onion breeding.
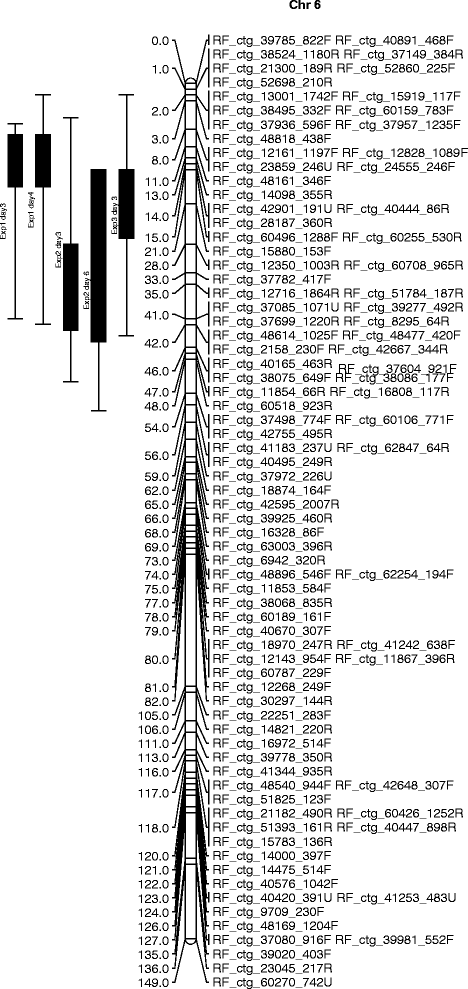
Results: Transcriptome sequencing resulted in 192 million RNA seq reads from the interspecific F1 hybrid between A. roylei and A. fistulosum (RF) and nine onion cultivars. After assembly, reliable SNPs were discovered in about 36 % of the contigs. For genotyping of the interspecific three-way cross population, derived from a cross between an onion cultivar and the RF (CCxRF), 1100 SNPs that are polymorphic in RF and monomorphic in the onion cultivars (RF SNPs) were selected for the development of KASP assays. A molecular linkage map based on 667 RF-SNP markers was constructed for CCxRF. In addition, KASP assays were developed for 1600 onion-SNPs (SNPs polymorphic among onion cultivars). A second linkage map was constructed for an F2 of onion x A. roylei (F2(CxR)) that consisted of 182 onion-SNPs and 119 RF-SNPs, and 76 previously mapped markers. Markers co-segregating in both the F2(CxR) and the CCxRF population were used to assign the linkage groups of RF to onion chromosomes. To validate usefulness of these SNP markers, QTL mapping was applied in the CCxRF population that segregates for resistance to Botrytis squamosa and resulted in a QTL for resistance on chromosome 6 of A. roylei.
Conclusions: Our research has more than doubled the publicly available marker sequences of expressed onion genes and two onion-related species. It resulted in a detailed genetic map for the interspecific CCxRF population. This is the first paper that reports the detection of a QTL for resistance to B. squamosa in A. roylei.
Keywords: A. fistulosum; A. roylei; Allium cepa; Botrytis squamosa; Interspecific hybrids; Transcriptome sequencing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Construction of a high-density linkage map and graphical representation of the arrangement of transcriptome-based unigene markers on the chromosomes of onion, Allium cepa L.BMC Genomics. 2021 Jun 26;22(1):481. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07803-y. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34174821 Free PMC article.
-
AlliumMap-A comparative genomics resource for cultivated Allium vegetables.BMC Genomics. 2012 May 4;13:168. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-168. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22559261 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of the interaction between Allium species and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi.Theor Appl Genet. 2011 Mar;122(5):947-60. doi: 10.1007/s00122-010-1501-8. Epub 2011 Jan 11. Theor Appl Genet. 2011. PMID: 21222096 Free PMC article.
-
[Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and its application in rice].Yi Chuan. 2006 Jun;28(6):737-44. Yi Chuan. 2006. PMID: 16818440 Review. Chinese.
-
Peeling the Onion: Towards a Better Understanding of Botrytis Diseases of Onion.Phytopathology. 2021 Mar;111(3):464-473. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-06-20-0258-IA. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Phytopathology. 2021. PMID: 32748737 Review.
Cited by
-
Omics approaches in Allium research: Progress and way ahead.PeerJ. 2020 Sep 9;8:e9824. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9824. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32974094 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of an Onion (Allium cepa L.) Genetic Linkage Map using Genotyping-by-Sequencing Analysis with a Reference Gene Set and Identification of QTLs Controlling Anthocyanin Synthesis and Content.Plants (Basel). 2020 May 12;9(5):616. doi: 10.3390/plants9050616. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32408580 Free PMC article.
-
Proportion of parental genomes in hybrids Allium cepa × A. roylei determines which one becomes dominant.Plant Genome. 2025 Jun;18(2):e70016. doi: 10.1002/tpg2.70016. Plant Genome. 2025. PMID: 40156203 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation and Global Distribution of Onion (Allium cepa L.) Germplasm for Agricultural Sustainability.Plants (Basel). 2023 Sep 18;12(18):3294. doi: 10.3390/plants12183294. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering genetic diversity phylogeny and assembly of Allium species through micro satellite markers on nuclear DNA.Heliyon. 2024 May 21;10(11):e31650. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31650. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38845887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- FAOSTAT. © FAO. Production quantities by country. 2014. faostat3.fao.org.
-
- Shigyo, Kik . Onion. In: Prohens J, Nuez F, editors. Vegetables II: Fabaceae, Liliaceae, Umbelliferae and Solanaceae (Handbook of plant breeding) New York: Springer; 2008. pp. 121–159.
-
- Broekgaarden C, Snoeren TAL, Dicke M, Vosman B. Exploiting natural variation to identify insect-resistance genes. Plant Biotechnol J. 2011;9:819–25. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7652.2011.00635.x. - PubMed
-
- Hajjar R, Hodgkin T. The use of wild relatives in crop improvement: a survey of developments over the last 20 years. Euphytica. 2007;156:1–13. doi:10.1007/s10681-007-9363-0.
-
- Kofoet A, Kik C, Wietsma WA, de Vries JN. Inheritance of resistance to downy mildew from Allium roylei Stearn in the backcross Allium cepa x (A. roylei x A. cepa) Plant Breed. 1990;105:144–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0523.1990.tb00467.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

