IGF-1R and mTOR Blockade: Novel Resistance Mechanisms and Synergistic Drug Combinations for Ewing Sarcoma
- PMID: 27576731
- PMCID: PMC5241894
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djw182
IGF-1R and mTOR Blockade: Novel Resistance Mechanisms and Synergistic Drug Combinations for Ewing Sarcoma
Abstract
Background: Therapies cotargeting insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF-1R) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) have demonstrated remarkable, albeit short-lived, clinical responses in a subset of Ewing sarcoma (ES) patients. However, the mechanisms of resistance and applicable strategies for overcoming drug resistance to the IGF-1R/mTOR blockade are still undefined.
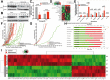
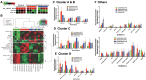
Methods: To elucidate predominant mechanism(s) of acquired drug resistance while identifying synergistic drug combinations that improve clinical efficacy, we generated more than 18 ES cell lines resistant to IGF-1R- or mTOR-targeted therapy. Two small-molecule inhibitors of IGF-1R were chosen, NVP-ADW-742 (IGF-1R-selective) and OSI-906 (a dual IGF-1R/insulin receptor alpha [IR-α] inhibitor). Reverse-phase protein lysate arrays (RPPAs) revealed proteomic changes linked to IGF-1R/mTOR resistance, and selected proteins were validated in cell-based assays, xenografts, and within human clinical samples. All statistical tests were two-sided.
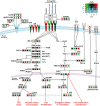
Results: Novel mechanisms of resistance (MOR) emerged after dalotuzumab-, NVP-ADW-742-, and OSI-906-based targeting of IGF-1R. MOR to dalotuzumab included upregulation of IRS1, PI3K, and STAT3, as well as p38 MAPK, which was also induced by OSI-906. pEIF4E(Ser209), a key regulator of Cap-dependent translation, was induced in ridaforolimus-resistant ES cell lines. Unique drug combinations targeting IGF-1R and PI3K-alpha or Mnk and mTOR were synergistic in vivo and vitro (P < .001) as assessed respectively by Mantel-Cox and isobologram testing.
Conclusions: We discovered new druggable targets expressed by chemoresistant ES cells, xenografts, and relapsed human tumors. Joint suppression of these newfound targets, in concert with IGF-1R or mTOR blockade, should improve clinical outcomes.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-targeting antibody, CP-751,871, suppresses tumor-derived VEGF and synergizes with rapamycin in models of childhood sarcoma.Cancer Res. 2009 Oct 1;69(19):7662-71. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1693. Epub 2009 Sep 29. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19789339 Free PMC article.
-
Ridaforolimus (MK-8669) synergizes with Dalotuzumab (MK-0646) in hormone-sensitive breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2016 Oct 20;16(1):814. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2847-3. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27765027 Free PMC article.
-
Dual treatments targeting IGF-1R, PI3K, mTORC or MEK synergize to inhibit cell growth, induce apoptosis, and arrest cell cycle at G1 phase in MDA-MB-231 cell line.Biomed Pharmacother. 2015 Oct;75:40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.08.031. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 26463630
-
Ewing sarcoma: The clinical relevance of the insulin-like growth factor 1 and the poly-ADP-ribose-polymerase pathway.Eur J Cancer. 2016 Jan;53:171-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.09.009. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Eur J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26765686 Review.
-
New strategies to overcome resistance to mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors in breast cancer.Curr Opin Oncol. 2013 Nov;25(6):587-93. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000014. Curr Opin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24097108 Review.
Cited by
-
The Interplay Between Non-coding RNAs and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Signaling in the Pathogenesis of Neoplasia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 9;9:634512. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.634512. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33768092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of ARID1A in the Nonestrogenic Modulation of IGF-1 Signaling.Mol Cancer Res. 2022 Jul 6;20(7):1071-1082. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-21-0961. Mol Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35320351 Free PMC article.
-
Costs and Causes of Oncology Drug Attrition With the Example of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Inhibitors.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jul 3;6(7):e2324977. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.24977. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37505498 Free PMC article.
-
IGF1R immunohistochemistry in Ewing's sarcoma as predictor of response to targeted therapy.Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2020 Jul-Aug;14(4):17-21. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2020. PMID: 32694968 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Tyrosine Kinases as a Critical Prognostic Parameter and Its Targeted Therapies in Ewing Sarcoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 9;8:613. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00613. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32754598 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kolb EA, Gorlick R. Development of IGF-IR Inhibitors in Pediatric Sarcomas. Curr Oncol Rep. 2009;11(4):307–313. - PubMed
-
- Tolcher AW, Sarantopoulos J, Patnaik A, et al. Phase I, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of AMG 479, a fully human monoclonal antibody to insulin-like growth factor receptor 1. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(34):5800–5807. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

