Anti-VEGF treatment is the key strategy for neovascular glaucoma management in the short term
- PMID: 27576739
- PMCID: PMC5006321
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-016-0327-9
Anti-VEGF treatment is the key strategy for neovascular glaucoma management in the short term
Abstract
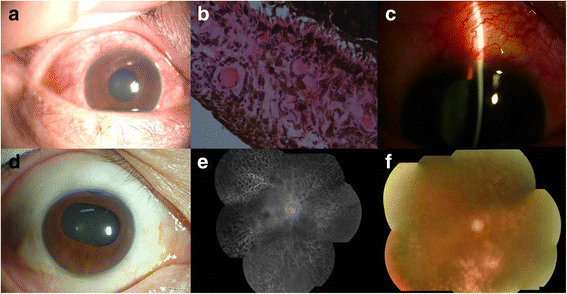
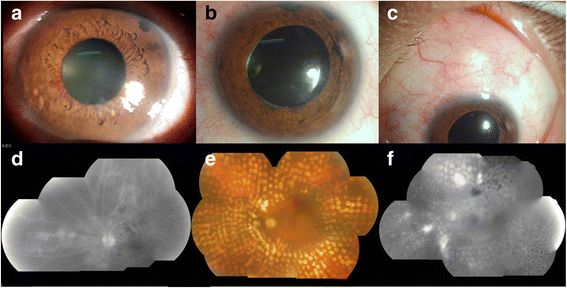
Background: To present a comprehensive approach for the management of patients with neovascular glaucoma (NVG) aiming to preserve visual function and complement pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP) by anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) treatment and anti-glaucoma surgery.
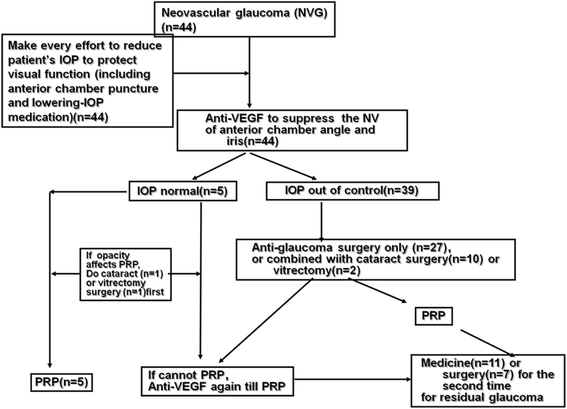
Methods: This study includes a prospective, interventional case series. A process flow chart for NVG management was designed. Totally 50 patients (51 eyes) with NVG were included. Of these, 43 patients (44 eyes) completed the treatment process. Patients were divided into central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO) and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) groups according to their original diagnosis. Intraocular pressure (IOP), visual function, and the status of iris and angle neovascularization were recorded before and after treatment.
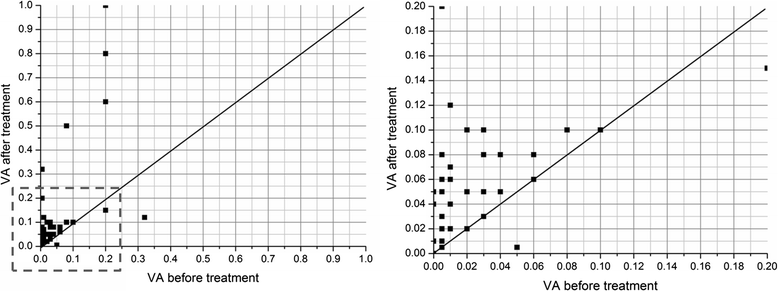
Results: Patients were followed up for 6-30 months (mean 12.2 months). The IOP of all 44 patients was effectively controlled and was significantly less after treatment (16.68 ± 4.69 mmHg) than before treatment (42.59 ± 9.44 mmHg, P < 0.05). Thirty-nine eyes displayed controlled IOP (≤21 mmHg) after treatment. Visual acuity improved, to some extent, in 32 eyes (72.9 %), and 12 eyes (27.3 %) had a visual acuity better than 0.1. There was no significant difference in IOP between the PDR and CRVO groups at the end of follow-up (P = 0.8657), but the visual acuity in the PDR group was much better than that in the CRVO group (P = 0.0079).
Conclusions: A comprehensive therapy for NVG can effectively control IOP and preserve visual function in patients by anti-VEGF injection and anti-glaucoma surgery.
Keywords: Anti-VEGF therapy; Anti-glaucoma surgery; Neovascular glaucoma; Pan-retinal photocoagulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intravitreal bevacizumab to treat iris neovascularization and neovascular glaucoma secondary to ischemic retinal diseases in 41 consecutive cases.Ophthalmology. 2008 Sep;115(9):1571-80, 1580.e1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.02.026. Epub 2008 Apr 28. Ophthalmology. 2008. PMID: 18440643
-
Clinical and electrophysiologic outcome in patients with neovascular glaucoma treated with and without bevacizumab.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2012 Jul-Aug;22(4):563-74. doi: 10.5301/ejo.5000089. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 22139613 Clinical Trial.
-
[Results of trabeculectomy with anti-VGEF therapy in the treatment of neovascular glaucoma secondary to retinal vein occlusion (report of 21 cases followed at Bukavu Eye Clinic from January 1 to December 31th, 2015)].J Fr Ophtalmol. 2017 Jan;40(1):17-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2016.08.009. Epub 2016 Nov 22. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2017. PMID: 27884546 Clinical Trial. French.
-
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for neovascular glaucoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Feb 6;2(2):CD007920. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007920.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Apr 3;4:CD007920. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007920.pub4. PMID: 32027392 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
-
A review of neovascular glaucoma. Etiopathogenesis and treatment.Rom J Ophthalmol. 2021 Oct-Dec;65(4):315-329. doi: 10.22336/rjo.2021.66. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 35087972 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term surgical outcomes of Ahmed valve implantation in refractory glaucoma according to the type of glaucoma.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 Jun 20;22(1):270. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02493-w. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35725417 Free PMC article.
-
Betalain exerts a protective effect against glaucoma is majorly through the association of inflammatory cytokines.AMB Express. 2020 Jul 14;10(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13568-020-01062-y. AMB Express. 2020. PMID: 32666339 Free PMC article.
-
Role of bevacizumab intraocular injection in the management of neovascular glaucoma.Int J Ophthalmol. 2021 Jun 18;14(6):855-859. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2021.06.10. eCollection 2021. Int J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34150540 Free PMC article.
-
Early vitrectomy combined with pan retinal photocoagulation, anti-vascular endothelial growth factor, and gradual cyclophotocoagulation for treatment of neovascular glaucoma.Chin Med J (Engl). 2019 Oct 20;132(20):2518-2520. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000482. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019. PMID: 31613817 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
23G Minimally Invasive Vitrectomy Combined with Glaucoma Drainage Valve Implantation and Phacoemulsification Cataract Extraction for Neovascular Glaucoma Secondary to Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy with Vitreous Hemorrhage.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Aug 4;2022:7393661. doi: 10.1155/2022/7393661. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jul 26;2023:9868749. doi: 10.1155/2023/9868749. PMID: 35966245 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wakabayashi T, Oshima Y, Sakaguchi H, Ikuno Y, Miki A, Gomi F, Otori Y, Kamei M, Kusaka S, Tano Y. Intravitreal bevacizumab to treat iris neovascularization and neovascular glaucoma secondary to ischemic retinal diseases in 41 consecutive cases. Ophthalmology. 2008;115(9):1571–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.02.026. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Konareva-Kostianeva M. Neovascular glaucoma. Folia Med (Plovdiv) 2005;47(2):5–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

