Investigation of the Immunomodulatory effect of Berberis vulgaris on core-pulsed dendritic cell vaccine
- PMID: 27577059
- PMCID: PMC5004255
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1327-2
Investigation of the Immunomodulatory effect of Berberis vulgaris on core-pulsed dendritic cell vaccine
Abstract
Background: Virus-induced dendritic cells (DCs) functional deficiency leads to sub-optimal initiation of adaptive immune responses and consequently chronic infection establishment. The present study reports an advanced hepatitis C virus (HCV) therapeutic vaccine model based on In vivo enrichment of DCs with barberry ethanolic crude extract (BCE) then pulsing them with HCV core protein.
Methods: DCs were enriched by BCE intravenous injection in BALB/c mice. Vaccine efficiency was assessed by flow cytometric analysis of splenocytes of immunized mice, cytokine profiling, cytotoxic T lymphocyte assay, and humoral immune response assessment.
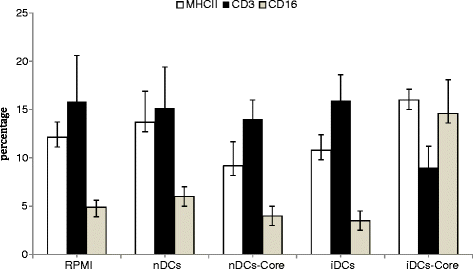
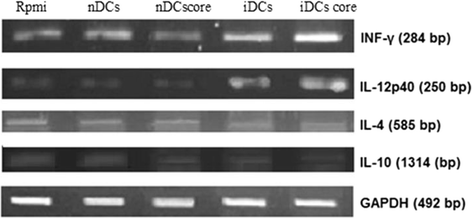
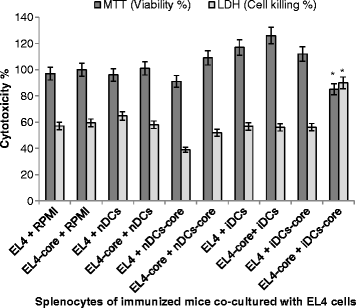
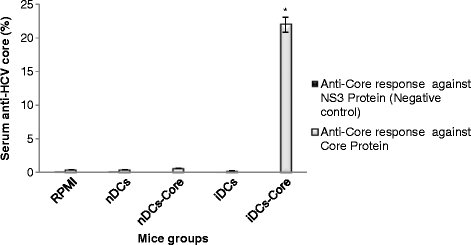
Results: There was no significant difference in surface phenotypic characterization of splenocytes from mice immunized with non-BCE-enriched-core-pulsed DCs (iDcs-core) compared to those from mice injected with RPMI-1640 medium. However, splenocytes from mice immunized with BCE-enriched-core-pulsed DCs showed 197 % increase in CD16+ population, 33 % increase in MHCII(+) population, and 43 % decrease in CD3(+) population. In iDCs-core group, 57.9 % greater anti-core cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity, up-regulation in interferon gamma and interleukin (IL) -12 expression, and down-regulation in IL-4 and IL-10 were recorded. Moreover, sustained specific anti-core antibodies were detected only in sera of the same group.
Conclusions: results indicate that BCE-enriched-core-transduced DCs may serve as a new model for immunotherapy of HCV chronic infection.
Keywords: Berberis vulgaris; IL 12; IL 4; INF-γ; Th-1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vaccination with protein-transduced dendritic cells elicits a sustained response to hepatitis C viral antigens.Gastroenterology. 2006 Feb;130(2):453-64. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.10.048. Gastroenterology. 2006. PMID: 16472599
-
Prophylactic and therapeutic vaccination with dendritic cells against hepatitis C virus infection.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Nov;142(2):362-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02919.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16232225 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant HCV core protein and the secretion of associated cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α and IFN-γ) in immunized mice.Pak J Biol Sci. 2013 Dec 15;16(24):2041-5. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2013.2041.2045. Pak J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24517026
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Barberry (Berberis vulgaris) and Its Main Compounds.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 19;2019:6183965. doi: 10.1155/2019/6183965. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31827685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Berberis Vulgaris and Berberine: An Update Review.Phytother Res. 2016 Nov;30(11):1745-1764. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5693. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Phytother Res. 2016. PMID: 27528198 Review.
Cited by
-
MTBHsp70-exFPR1-pulsed Dendritic Cells Enhance the Immune Response against Cervical Cancer.J Cancer. 2019 Oct 19;10(25):6364-6373. doi: 10.7150/jca.29779. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31772669 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticles of ZnO/Berberine complex contract COVID-19 and respiratory co-bacterial infection in addition to elimination of hydroxychloroquine toxicity.J Pharm Investig. 2021;51(6):735-757. doi: 10.1007/s40005-021-00544-w. Epub 2021 Sep 6. J Pharm Investig. 2021. PMID: 34513113 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal Plants and Isolated Molecules Demonstrating Immunomodulation Activity as Potential Alternative Therapies for Viral Diseases Including COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2021 May 13;12:637553. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.637553. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054806 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coligan JE, Vogel S. Innate Immunity. In: Coligan JE, Bierer BE, Margulies DH, Shevach EM, Strober W, editors. Current Protocols in Immunology. Hoboken: Wiley; 2012. pp. 1401–1407.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

