A mixed method study exploring adherence to and acceptability of small quantity lipid-based nutrient supplements (SQ-LNS) among pregnant and lactating women in Ghana and Malawi
- PMID: 27577112
- PMCID: PMC5004276
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-016-1039-0
A mixed method study exploring adherence to and acceptability of small quantity lipid-based nutrient supplements (SQ-LNS) among pregnant and lactating women in Ghana and Malawi
Abstract
Background: Supplementing pregnant and lactating mothers with small quantity lipid-based nutrient supplements (SQ-LNS) has resulted in improvements in birth outcomes in some low-income settings. In order to be effective, SQ-LNS must be consumed regularly over sustained periods.
Methods: The objective was to assess and compare acceptability of and adherence to SQ-LNS consumption among pregnant and lactating women in Ghana and Malawi throughout 12 months of supplementation. We enrolled women before 20 gestation weeks into randomized trials in Ghana (n = 1320) and Malawi (n = 869). In the SQ-LNS group participants received a 20 g sachet of supplement per day during pregnancy and the first 6 months of lactation. In the control groups participants received multiple micronutrients (MMN) during pregnancy and lactation or iron and folic acid (IFA) during pregnancy and calcium during lactation. We used questionnaires to collect data on self-reported adherence to daily use of supplements and conducted in-depth interviews with women in the SQ-LNS group to examine acceptability.
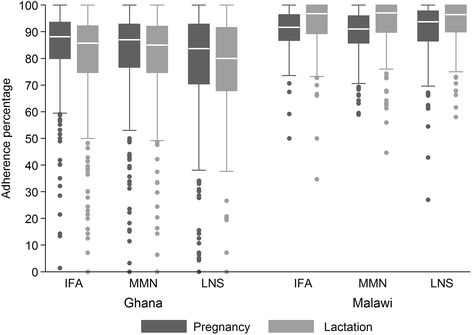
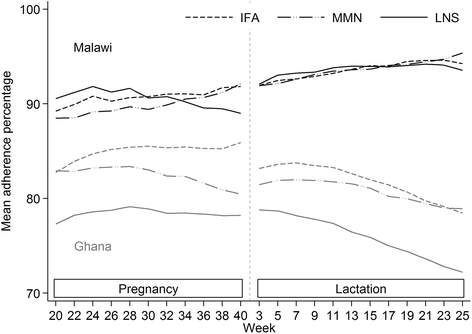
Results: The mean self-reported adherence during the supplementation period was lower in Ghana (79.9 %) than in Malawi (91.7 %) for all supplements (difference 11.8 %, P < 0.001). Over time, adherence increased in Malawi but decreased in Ghana. In both countries, adherence in the SQ-LNS group was non-inferior to that in the control groups. Participants typically reported consuming SQ-LNS as instructed but when interviewers queried about experiences, most of the women described incidents of non-adherence. A usual reason for not consuming SQ-LNS was nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. Especially in Malawi, women reported sharing SQ-LNS with families and friends. Sustained use of SQ-LNS was attributed to expected health benefits and favorable sensory attributes. Often women compared their pregnancy to previous ones, and were of the view that SQ-LNS made a positive difference.
Conclusion: Self-reported sustained adherence to consume SQ-LNS daily was high in both sites but lower in Ghana than in Malawi. In Ghana, adherence decreased over time whereas in Malawi adherence increased. Acceptability and adherence appeared interlinked, complex and context-related. Sustained consumption of SQ-LNS may require tailoring interventions by context.
Trial registration: The Ghana trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT00970866 , and the Malawi trial as NCT01239693 .
Keywords: Acceptability; Adherence; Ghana; Lactation; Malawi; Pregnancy; Small-quantity lipid-based nutrient supplements; Women.
Figures


References
-
- Abu-Saad K, Fraser D. Maternal nutrition and birth outcomes. Epidemiol Rev. 2004;32:2010. - PubMed
-
- Adu-Afarwuah S, Lartey A, Brown KH, Zlotkin S, Briend A, Dewey KG. Randomized comparison of 3 types of micronutrient supplements for home fortification of complementary foods in Ghana: effects on growth and motor development. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:412–20. - PubMed
-
- Adu-Afarwuah S, Lartey A, Okronipa H, Ashorn P, Peerson JM, Arimond M, Ashorn U, Zeilani M, Vosti S, Dewey KG. Small-quantity lipid-based nutrient supplements provided to women during pregnancy and 6 mo postpartum, and to their infants from 6 mo of age, increases child linear growth by 18 mo of age in semi-urban Ghana: A randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016. doi:10.3945/ajcn.116.134692. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

