High Fat Diet-Induced Skeletal Muscle Wasting Is Decreased by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Administration: Implications on Oxidative Stress, Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway Activation, and Myonuclear Apoptosis
- PMID: 27579157
- PMCID: PMC4992759
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9047821
High Fat Diet-Induced Skeletal Muscle Wasting Is Decreased by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Administration: Implications on Oxidative Stress, Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway Activation, and Myonuclear Apoptosis
Abstract
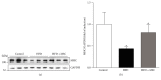
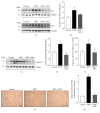
Obesity can lead to skeletal muscle atrophy, a pathological condition characterized by the loss of strength and muscle mass. A feature of muscle atrophy is a decrease of myofibrillar proteins as a result of ubiquitin proteasome pathway overactivation, as evidenced by increased expression of the muscle-specific ubiquitin ligases atrogin-1 and MuRF-1. Additionally, other mechanisms are related to muscle wasting, including oxidative stress, myonuclear apoptosis, and autophagy. Stem cells are an emerging therapy in the treatment of chronic diseases such as high fat diet-induced obesity. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a population of self-renewable and undifferentiated cells present in the bone marrow and other mesenchymal tissues of adult individuals. The present study is the first to analyze the effects of systemic MSC administration on high fat diet-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in the tibialis anterior of mice. Treatment with MSCs reduced losses of muscle strength and mass, decreases of fiber diameter and myosin heavy chain protein levels, and fiber type transitions. Underlying these antiatrophic effects, MSC administration also decreased ubiquitin proteasome pathway activation, oxidative stress, and myonuclear apoptosis. These results are the first to indicate that systemically administered MSCs could prevent muscle wasting associated with high fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes.
Figures





References
-
- Bhatt B. A., Dube J. J., Dedousis N., Reider J. A., O'Doherty R. M. Diet-induced obesity and acute hyperlipidemia reduce IκBα levels in rat skeletal muscle in a fiber-type dependent manner. American Journal of Physiology—Regulatory Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 2006;290(1):R233–R240. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00097.2005. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

