Role of milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 in osteoimmunology
- PMID: 27579162
- PMCID: PMC4954605
- DOI: 10.1038/bonekey.2016.52
Role of milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 in osteoimmunology
Abstract
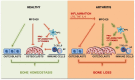
Milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 (MFG-E8) is a glycoprotein that is abundantly expressed in various tissues and has a pivotal role in the phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells. However, MFG-E8 has also gained significant attention because of its wide range of functions in autoimmunity, inflammation and tissue homeostasis. More recently, MFG-E8 has been identified as a critical regulator of bone homeostasis, being expressed in both, osteoblasts and osteoclasts. In addition, it was shown that MFG-E8 fulfils an active role in modulating inflammatory processes, suggesting an anti-inflammatory role of MFG-E8 and proposing it as a novel therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases. This concise review focusses on the expression and regulation of MFG-E8 in the context of inflammatory bone diseases, highlights its role in the pathophysiology of osteoimmune diseases and discusses the therapeutic potential of MFG-E8.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loss of milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 (MFG-E8) in mice leads to low bone mass and accelerates ovariectomy-associated bone loss by increasing osteoclastogenesis.Bone. 2015 Jul;76:107-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.04.003. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Bone. 2015. PMID: 25868798
-
Milk Fat Globule-Epidermal Growth Factor 8 (MFG-E8) Is a Novel Anti-inflammatory Factor in Rheumatoid Arthritis in Mice and Humans.J Bone Miner Res. 2016 Mar;31(3):596-605. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2721. Epub 2015 Nov 9. J Bone Miner Res. 2016. PMID: 26391522 Free PMC article.
-
MFG-E8, a novel homeostatic regulator of osteoclastogenesis.Inflamm Cell Signal. 2014;1(5):e285. doi: 10.14800/ics.285. Inflamm Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 26052544 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Role of Milk Fat Globule-Epidermal Growth Factor VIII in Macrophage-Mediated Inflammatory Responses and Inflammatory/Autoimmune Diseases.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:5628486. doi: 10.1155/2016/5628486. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27429513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurogenesis in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Role of MFG-E8.Front Neurosci. 2019 Jun 4;13:569. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00569. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31213977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synovial fluid and plasma levels of milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 are inversely correlated with radiographic severity of knee osteoarthritis.J Int Med Res. 2019 Sep;47(9):4422-4430. doi: 10.1177/0300060519862460. Epub 2019 Jul 25. J Int Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31342838 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of plasma exosomes in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 Jul;11(7):1434-1452. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-467. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35958340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanayama R, Tanaka M, Miwa K, Shinohara A, Iwamatsu A, Nagata S. Identification of a factor that links apoptotic cells to phagocytes. Nature 2002; 417: 182–187. - PubMed
-
- Hanayama R, Tanaka M, Miyasaka K, Aozasa K, Koike M, Uchiyama Y et al. Autoimmune disease and impaired uptake of apoptotic cells in MFG-E8-deficient mice. Science 2004; 304: 1147–1150. - PubMed
-
- Sinningen K, Albus E, Thiele S, Grossklaus S, Kurth T, Udey MC et al. Loss of milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 (MFG-E8) in mice leads to low bone mass and accelerates ovariectomy-associated bone loss by increasing osteoclastogenesis. Bone 2015; 76: 107–114. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
