Endoscopic Resection of a Pedunculated Brunner's Gland Hamartoma of the Duodenum
- PMID: 27579190
- PMCID: PMC4992794
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/6707235
Endoscopic Resection of a Pedunculated Brunner's Gland Hamartoma of the Duodenum
Abstract
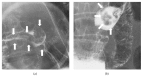
A 68-year-old Japanese woman presented with a solitary pedunculated polyp in the duodenum. Endoscopic ultrasonography showed multiple cystic structures in the polyp. The polyp was successfully resected by endoscopic snare polypectomy and pathologically diagnosed as Brunner's gland hamartoma. Because hamartomatous components were not identified in the stalk of the polyp, we speculate that the stalk developed from traction of the normal duodenal mucosa. When a solitary, pedunculated polyp with cystic structure within the submucosa is found in the duodenum, Brunner's gland hamartoma should be considered in the differential diagnosis, despite the rarity of the disease. This case underscores the usefulness of endoscopic ultrasonography for the diagnosis of duodenal subepithelial tumors.
Figures




References
-
- Muezzinoglu B., Ustun H., Demirhan B., Hilmioglu F. Brunner's gland adenoma: case report. New Zealand Medical Journal. 1995;108(992):p. 14. - PubMed
-
- Chattopadhyay P., Kundu A. K., Bhattacharyya S., Bandyopadhyay A. Diffuse nodular hyperplasia of Brunner's gland presenting as upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage. Singapore Medical Journal. 2008;49(1):81–83. - PubMed
-
- Levine J. A., Burgart L. J., Batts K. P., Wang K. K. Brunner's gland hamartomas: clinical presentation and pathological features of 27 cases. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 1995;90(2):290–294. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

