5-HT2A Receptor Binding in the Frontal Cortex of Parkinson's Disease Patients and Alpha-Synuclein Overexpressing Mice: A Postmortem Study
- PMID: 27579212
- PMCID: PMC4989080
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/3682936
5-HT2A Receptor Binding in the Frontal Cortex of Parkinson's Disease Patients and Alpha-Synuclein Overexpressing Mice: A Postmortem Study
Abstract
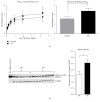
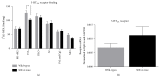
The 5-HT2A receptor is highly involved in aspects of cognition and executive function and seen to be affected in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's disease and related to the disease pathology. Even though Parkinson's disease (PD) is primarily a motor disorder, reports of impaired executive function are also steadily being associated with this disease. Not much is known about the pathophysiology behind this. The aim of this study was thereby twofold: (1) to investigate 5-HT2A receptor binding levels in Parkinson's brains and (2) to investigate whether PD associated pathology, alpha-synuclein (AS) overexpression, could be associated with 5-HT2A alterations. Binding density for the 5-HT2A-specific radioligand [(3)H]-MDL 100.907 was measured in membrane suspensions of frontal cortex tissue from PD patients. Protein levels of AS were further measured using western blotting. Results showed higher AS levels accompanied by increased 5-HT2A receptor binding in PD brains. In a separate study, we looked for changes in 5-HT2A receptors in the prefrontal cortex in 52-week-old transgenic mice overexpressing human AS. We performed region-specific 5-HT2A receptor binding measurements followed by gene expression analysis. The transgenic mice showed lower 5-HT2A binding in the frontal association cortex that was not accompanied by changes in gene expression levels. This study is one of the first to look at differences in serotonin receptor levels in PD and in relation to AS overexpression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in 5-HT2A receptor expression in untreated, de novo patients with Parkinson's disease.J Parkinsons Dis. 2014;4(2):283-7. doi: 10.3233/JPD-130300. J Parkinsons Dis. 2014. PMID: 24398658
-
Phosphorylation of tau and alpha-synuclein in synaptic-enriched fractions of the frontal cortex in Alzheimer's disease, and in Parkinson's disease and related alpha-synucleinopathies.Neuroscience. 2008 Apr 9;152(4):913-23. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.030. Epub 2008 Feb 5. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18343584
-
Parkinson's disease and alpha synuclein: is Parkinson's disease a prion-like disorder?Mov Disord. 2013 Jan;28(1):31-40. doi: 10.1002/mds.25373. Mov Disord. 2013. PMID: 23390095 Review.
-
Mitochondrial associated metabolic proteins are selectively oxidized in A30P alpha-synuclein transgenic mice--a model of familial Parkinson's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2005 Apr;18(3):492-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2004.12.009. Neurobiol Dis. 2005. PMID: 15755676
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
Cited by
-
Parkinson disease psychosis: from phenomenology to neurobiological mechanisms.Nat Rev Neurol. 2024 Mar;20(3):135-150. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00918-8. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Nat Rev Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38225264 Review.
-
Relevance of 5-HT2A Receptor Modulation of Pyramidal Cell Excitability for Dementia-Related Psychosis: Implications for Pharmacotherapy.CNS Drugs. 2021 Jul;35(7):727-741. doi: 10.1007/s40263-021-00836-7. Epub 2021 Jul 5. CNS Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34224112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal models of α-synucleinopathy for Parkinson disease drug development.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017 Sep;18(9):515-529. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.75. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28747776 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

