Toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases: recent and emerging translational developments
- PMID: 27579291
- PMCID: PMC5001654
- DOI: 10.2147/ITT.S89795
Toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases: recent and emerging translational developments
Abstract
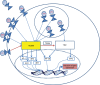
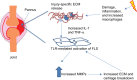
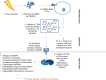
Autoinflammatory diseases are defined as the loss of self-tolerance in which an inflammatory response to self-antigens occurs, which are a significant global burden. Toll-like receptors are key pattern recognition receptors, which integrate signals leading to the activation of transcription factors and ultimately proinflammatory cytokines. Recently, it has become apparent that these are at the nexus of autoinflammatory diseases making them viable and attractive drug targets. The aim of this review was to evaluate the role of innate immunity in autoinflammatory conditions alongside the role of negative regulation while suggesting possible therapeutic targets.
Keywords: arthritis; autoimmunity; danger signals; toll-like receptors.
Figures
References
-
- Fullard N, O’Reilly S. Role of innate immune system in systemic sclerosis. Semin Immunopathol. 2015;37(5):511–517. - PubMed
-
- Too LK, McGregor IS, Baxter AG, Hunt NH. Altered behaviour and cognitive function following combined deletion of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in mice. Behav Brain Res. 2016;303:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Škanta F, Roubalová R, Dvořák J, Procházková P, Bilej M. Molecular cloning and expression of TLR in the Eisenia andrei earthworm. Dev Comp Immunol. 2013;41(4):694–702. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA., Jr A human homologue of the drosophila toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature. 1997;388(6640):394–397. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

