Skin barrier in atopic dermatitis: beyond filaggrin
- PMID: 27579743
- PMCID: PMC4999106
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20164412
Skin barrier in atopic dermatitis: beyond filaggrin
Abstract
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease with a complex pathogenesis, where changes in skin barrier and imbalance of the immune system are relevant factors. The skin forms a mechanic and immune barrier, regulating water loss from the internal to the external environment, and protecting the individual from external aggressions, such as microorganisms, ultraviolet radiation and physical trauma. Main components of the skin barrier are located in the outer layers of the epidermis (such as filaggrin), the proteins that form the tight junction (TJ) and components of the innate immune system. Recent data involving skin barrier reveal new information regarding its structure and its role in the mechanic-immunological defense; atopic dermatitis (AD) is an example of a disease related to dysfunctions associated with this complex.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
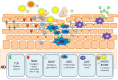
 Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus),
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus),  Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis),
Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis),
 other
bacteria,
other
bacteria,  staphylococcal enterotox in,
staphylococcal enterotox in,  virus,
virus,  Toll-like receptors (TLR),
Toll-like receptors (TLR),  nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing
protein (NOD)
nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing
protein (NOD)  NOD-like receptor protein (NLRP)
NOD-like receptor protein (NLRP)  β-defensina 1,
β-defensina 1,
 HBD-2,3 e
LL37,
HBD-2,3 e
LL37,  inflammatory dendritic epidermal cells (IDEC),
inflammatory dendritic epidermal cells (IDEC),
 plasmacytoid DC (pDC).
plasmacytoid DC (pDC).Similar articles
-
Epidermal tight junction barrier function is altered by skin inflammation, but not by filaggrin-deficient stratum corneum.J Dermatol Sci. 2015 Jan;77(1):28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2014.11.007. Epub 2014 Nov 22. J Dermatol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25511077
-
Epidermal barrier dysfunction and cutaneous sensitization in atopic diseases.J Clin Invest. 2012 Feb;122(2):440-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI57416. Epub 2012 Feb 1. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22293182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atopic dermatitis: a disease of altered skin barrier and immune dysregulation.Immunol Rev. 2011 Jul;242(1):233-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01027.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21682749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin barrier in atopic dermatitis.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014 Jan 1;19(3):542-56. doi: 10.2741/4225. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014. PMID: 24389202 Review.
-
The cutaneous innate immune response in patients with atopic dermatitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Feb;131(2):266-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.12.1563. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23374259 Review.
Cited by
-
Atopic dermatitis: pathogenesis and therapeutic intervention.MedComm (2020). 2024 Dec 8;5(12):e70029. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70029. eCollection 2024 Dec. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39654684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic Implications of Bullous Pemphigoid: Bridging Dermatology and Internal Medicine.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;14(20):2272. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14202272. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FRA1:c-JUN:HDAC1 complex down-regulates filaggrin expression upon TNFα and IFNγ stimulation in keratinocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Sep 13;119(37):e2123451119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2123451119. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36067301 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Vitamin C in Skin Diseases.Front Physiol. 2018 Jul 4;9:819. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00819. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30022952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ozonated Sunflower Oil (OSO) Alleviates Inflammatory Responses in Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis (AD)-Like Mice and LPS-Treated RAW 264.7 Cells.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Apr 28;34(4):765-773. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2310.10037. Epub 2024 Jan 12. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38247218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kapoor R, Menon C, Hoffstad O, Bilker W, Leclerc P, Margolis DJ. The prevalence of atopic triad in children with physician-confirmed atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:68–73. - PubMed
-
- Odhiambo JA, Williams HC, Clayton TO, Robertson CF, Asher MI, Group IPTS Global variations in prevalence of eczema symptoms in children from ISAAC Phase Three. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:1251–1258. e23. - PubMed
-
- Addor FA, Aoki V. Skin barrier in atopic dermatitis. An Bras Dermatol. 2010;85:184–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
