Diagnostic Value of Conventional Ultrasonography Combined with Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography in Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS) 3 and 4 Thyroid Micronodules
- PMID: 27580248
- PMCID: PMC5015597
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.897011
Diagnostic Value of Conventional Ultrasonography Combined with Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography in Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS) 3 and 4 Thyroid Micronodules
Abstract
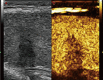
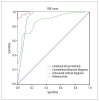
BACKGROUND The present study was conducted to investigate the diagnostic performance of conventional ultrasonography (US) combined with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) in thyroid micronodules with thyroid imaging reporting and data system (TI-RADS) category 3 and 4. MATERIAL AND METHODS The features of conventional US and CEUS ion 102 case of thyroid micronodule samples, which were diagnosed based on pathological and clinical examination, were retrospectively analyzed. Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the diagnostic accuracy in malignant thyroid micronodules. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve was used to assess the performance of those 2 technologies. RESULTS A significant difference in age was found between the benign and malignant groups. The benign and malignant groups showed significant differences in shape, margin, aspect ratio (A/T) ≥1, microcalcification, suspicious lymph gland, enhancement time, enhancement pattern, enhancement intensity, nodule sizes, enhancement margins, and rim-like enhancement. Logistic regression analysis of conventional US showed that A/T ≥1, irregular shape, microcalcification, and suspicious lymph glands are risk factors for thyroid micronodules, while logistic regression analysis of CEUS showed that slow enhancement time and absence of rim-like enhancement are risk factors for thyroid micronodules. Logistic regression analysis of conventional US combined with CEUS demonstrated that A/T ≥1, microcalcification, suspicious lymph gland, slow enhancement time, and absence with rim-like enhancement are risk factors. The ROC curve for conventional US, CEUS, and conventional US combined with CEUS were 90.0%, 90.7%, 99.0%, respectively. CONCLUSIONS Our results show that conventional US combined with CEUS had superior diagnostic performance for TI-RADS 3 and 4 thyroid micronodules compared with conventional US and CEUS alone.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Clinical diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and TI-RADS classification for benign and malignant thyroid tumors: One comparative cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jan;98(4):e14051. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014051. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30681562 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diagnostic performance of thyroid imaging reporting and data system (TI-RADS) alone and in combination with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for the characterization of thyroid nodules.Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2019;72(1):95-106. doi: 10.3233/CH-180457. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2019. PMID: 30320563
-
Diagnostic efficacy of CEUS TI-RADS classification for benign and malignant thyroid nodules.Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2025;89(1):27-41. doi: 10.3233/CH-232080. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2025. PMID: 39911118
-
Performance of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in assessing thyroid nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis using histological standard of reference.Radiol Med. 2020 Apr;125(4):406-415. doi: 10.1007/s11547-019-01129-2. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Radiol Med. 2020. PMID: 31970579
-
Performance of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in Thyroid Nodules: Review of Current State and Future Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 30;13(21):5469. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215469. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771632 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Taller-than-wide Thyroid Nodules With Microcalcifications Are at High Risk of Malignancy.In Vivo. 2020 Jul-Aug;34(4):2101-2105. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12014. In Vivo. 2020. PMID: 32606189 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and TI-RADS classification for benign and malignant thyroid tumors: One comparative cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jan;98(4):e14051. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014051. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30681562 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Computer-aided diagnosis of malignant or benign thyroid nodes based on ultrasound images.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Jul;274(7):2891-2897. doi: 10.1007/s00405-017-4562-3. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 28389809
-
Biomarkers of microvascularture by ultra Micro-angiography (UMA) assist to identify papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) with atypia of undetermined significance.BMC Cancer. 2025 May 1;25(1):819. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14197-7. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40312320 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performances of the KWAK-TIRADS classification, elasticity score, and Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology of TI-RADS category 4 thyroid nodules.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020 May 1;13(5):1159-1168. eCollection 2020. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32509090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pacini F. Thyroid microcarcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;26:421–29. - PubMed
-
- Tarrar AM, Wahla MS, Ilyas S, et al. Solitary thyroid nodule; Frequency of malignancy at combined Military Hospital Rawalpindi. Professional Medical Journal. 2010;17:598.
-
- Russ G, Bigorgne C, Royer B, et al. [The Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TIRADS) for ultrasound of the thyroid]. J Radiol. 2011;92:701–13. [in French] - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

