Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in rosacea: study protocol for a systematic review of the literature and identification of a core outcome set using a Delphi survey
- PMID: 27580586
- PMCID: PMC5007842
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1554-3
Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in rosacea: study protocol for a systematic review of the literature and identification of a core outcome set using a Delphi survey
Abstract
Background: Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting millions of individuals worldwide. Diagnosis is based on signs and symptoms with management and treatment aimed to suppress inflammatory lesions, erythema, and telangiectasia. While many clinical trials of rosacea exist, the lack of consensus in outcome reporting across all trials poses a concern. Proper evaluation and comparison of treatment modalities is challenging. In order to address the inconsistencies present, this project aims to determine a core set of outcomes which should be evaluated in all clinical trials of rosacea.
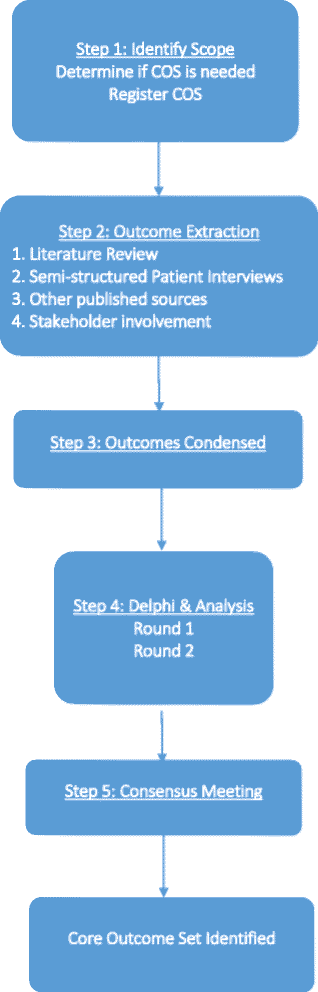
Methods/design: This project will utilize a methodology similar to previous core outcome set research. A long list of outcomes will be extracted over four phases: (1) systematic literature review, (2) patient interviews, (3) other published sources, and (4) stakeholder involvement. Potential outcomes will be examined by the Steering Committee to provide further insight. The Delphi process will then be performed to prioritize and condense the list of outcomes generated. Two homogenous groups of physicians and patients will participate in two consecutive rounds of Delphi surveys. A consensus meeting, composed of physicians, patients, and stakeholders, will be conducted after the Delphi exercise to further select outcomes, taking into account participant scores. By the end of the meeting, members will vote and decide on a final recommended set of core outcomes. For the duration of the study, we will be in collaboration with both the Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials (COMET) and Cochrane Skin Group - Core Outcome Set Initiative (CSG-COUSIN).
Discussion: This study aims to develop a core outcome set to guide assessment in clinical trials of rosacea. The end-goal is to improve the reliability and consistency of outcome reporting, thereby allowing sufficient evaluation of treatment effectiveness and patient satisfaction.
Keywords: Consensus; Core outcome set; Delphi; Rosacea; Stakeholders; Systematic review.
Similar articles
-
Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in basal cell carcinoma: study protocol for a systematic review of the literature and identification of a core outcome set using a Delphi survey.Trials. 2017 Oct 23;18(1):490. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2244-5. Trials. 2017. PMID: 29061190 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in facial aging: study protocol for a systematic review of the literature and identification of a core outcome set using a Delphi survey.Trials. 2017 Aug 1;18(1):359. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2104-3. Trials. 2017. PMID: 28764734 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in squamous cell carcinoma: study protocol for a systematic review of the literature and identification of a core outcome set using a Delphi survey.Trials. 2017 Jul 12;18(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2069-2. Trials. 2017. PMID: 28701207 Free PMC article.
-
Acne scarring: protocol for development of a core outcome set for clinical trials.BMJ Open. 2025 Apr 29;15(4):e088049. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-088049. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40306913 Free PMC article.
-
Rosacea Core Domain Set for Clinical Trials and Practice: A Consensus Statement.JAMA Dermatol. 2024 Jun 1;160(6):658-666. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2024.0636. JAMA Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38656294
Cited by
-
Protocol for the development of a core outcome set for reporting outcomes of management of velopharyngeal dysfunction.BMJ Open. 2020 Aug 13;10(8):e036824. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-036824. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32792441 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol for development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in melasma.BMJ Open. 2022 Feb 4;12(2):e046953. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-046953. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35121595 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in inflammatory bowel disease: study protocol for a systematic review of the literature and identification of a core outcome set using a Delphi survey.BMJ Open. 2017 Jun 9;7(6):e016146. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016146. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28601837 Free PMC article.
-
A core outcome set for clinical trials of first- and second-degree perineal tears prevention and treatment: a study protocol for a systematic review and a Delphi survey.Trials. 2021 Nov 25;22(1):843. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05820-6. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34823584 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Utility of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) for Facial Aging: A Comprehensive Review.Adv Ther. 2022 Sep;39(9):4021-4036. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02239-6. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35870104 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical