Rates of prostate surgery and acute urinary retention for benign prostatic hyperplasia in men treated with dutasteride or finasteride
- PMID: 27580700
- PMCID: PMC5006364
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-016-0170-6
Rates of prostate surgery and acute urinary retention for benign prostatic hyperplasia in men treated with dutasteride or finasteride
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have suggested a greater benefit for various outcomes in men diagnosed with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) who are treated with dutasteride than for men treated with finasteride. This study investigates whether the rates of BPH-related prostate surgery and acute urinary retention (AUR) differ between dutasteride and finasteride users in the Netherlands.
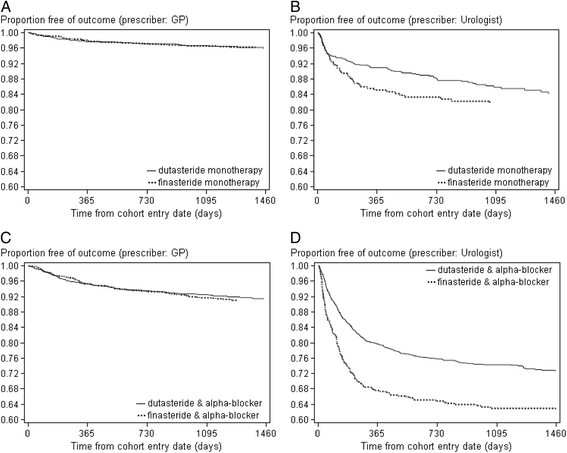
Methods: From the PHARMO Database Network, men aged ≥50 years with a dispensing of dutasteride or finasteride with or without concomitant alpha-blocker treatment between March 1, 2003 and December 31, 2011 were selected. The incidence of BPH-related prostate surgery and AUR was determined during dutasteride or finasteride treatment and stratified by type of initial BPH-treatment (5-ARI monotherapy or combination with alpha-blocker) and prescriber (general practitioner (GP) or urologist). Comparison of the incidence of BPH-related prostate surgery and AUR between the treatment groups was done by Cox proportional hazard regression.
Results: 11,822 dutasteride users and 5,781 finasteride users were identified. Most users started treatment in combination with an alpha-blocker. Overall, dutasteride users had a lower risk of BPH-related prostate surgery was lower among dutasteride users than finasteride users (HR: 0.75; 95 % CI: 0.56-0.99). This lower risk among dutasteride users was also seen when stratifying by monotherapy or combination therapy (HR: 0.73; 95 % CI: 0.54-0.98 for monotherapy and HR: 0.85; 95 % CI: 0.74-0.97 for combination therapy). However, the association was only present among men treated by urologists. For AUR the rates were low and no statistical significant difference was observed between dutasteride and finasteride users.
Conclusions: The risk of undergoing BPH-related prostate surgery was lower among men using dutasteride compared to men using finasteride. The association was observed for monotherapy as well as combination therapy, however, only among men who received their prescription from a urologist.
Keywords: 5-alpha reductase inhibitors; Acute urinary retention; Alpha-blocker; Benign prostatic hyperplasia; Prostate surgery.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: Rates of Prostate Surgery and Acute Urinary Retention for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Men Treated with Dutasteride or Finasteride.J Urol. 2017 Oct;198(4):719-721. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.07.003. Epub 2017 Jul 7. J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28905745 No abstract available.
-
Re: Analysis of Risk Factors Leading to Postoperative Urethral Stricture and Bladder Neck Contracture following Transurethral Resection of Prostate.J Urol. 2017 Oct;198(4):720-721. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.07.005. Epub 2017 Jul 7. J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28905747 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Comparing Clinical and Economic Outcomes Associated with Early Initiation of Combination Therapy of an Alpha Blocker and Dutasteride or Finasteride in Men with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in the United States.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016 Oct;22(10):1204-14. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2016.22.10.1204. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27668569 Free PMC article.
-
A large retrospective analysis of acute urinary retention and prostate-related surgery in BPH patients treated with 5-alpha reductase inhibitors: dutasteride versus finasteride.Am J Manag Care. 2007 Feb;13 Suppl 1:S10-6. Am J Manag Care. 2007. PMID: 17295600
-
Clinical outcomes after combined therapy with dutasteride plus tamsulosin or either monotherapy in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) by baseline characteristics: 4-year results from the randomized, double-blind Combination of Avodart and Tamsulosin (CombAT) trial.BJU Int. 2011 Mar;107(6):946-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10124.x. Epub 2011 Feb 18. BJU Int. 2011. PMID: 21332630 Clinical Trial.
-
Monotherapy versus combination drug therapy for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2005 Jun;3(2):103-14. doi: 10.1016/s1543-5946(05)00031-0. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2005. PMID: 16129387 Review.
-
Current Pharmacological Treatment for Male LUTS due to BPH: Dutasteride or Finasteride?Curr Drug Targets. 2015;16(11):1165-71. doi: 10.2174/1389450116666150518101617. Curr Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25981606 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of early vs. delayed initiation of dutasteride/tamsulosin combination therapy on the risk of acute urinary retention or BPH-related surgery in LUTS/BPH patients with moderate-to-severe symptoms at risk of disease progression.World J Urol. 2021 Jul;39(7):2635-2643. doi: 10.1007/s00345-020-03517-0. Epub 2020 Dec 18. World J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33337513 Free PMC article.
-
Stereological comparison of intraprostatic injection of alcohol and bleomycin with finasteride gavages in rats.Cent European J Urol. 2017 Jun 30;70(2):163-169. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2017.1211. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Cent European J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28721283 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription Trends of Initial Pharmacotherapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Among Treatment-Naïve Patients in South Korea: A Retrospective Analysis.Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2025 Sep;17(5):e70030. doi: 10.1111/luts.70030. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2025. PMID: 40908864 Free PMC article.
-
Existing Data Sources for Clinical Epidemiology: The PHARMO Database Network.Clin Epidemiol. 2020 Apr 29;12:415-422. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S247575. eCollection 2020. Clin Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 32425609 Free PMC article.
-
Model-based meta-analysis of the time to first acute urinary retention or benign prostatic hyperplasia-related surgery in patients with moderate or severe symptoms.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Jul;87(7):2777-2789. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14682. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33247951 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL. The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol. 1984;132:474–479. - PubMed
-
- Roehrborn CG, Oyarzabal Perez I, Roos EP, Calomfirescu N, Brotherton B, Wang F, Palacios JM, Vasylyev A, Manyak MJ. Efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination of dutasteride and tamsulosin treatment (Duodart((R))) compared with watchful waiting with initiation of tamsulosin therapy if symptoms do not improve, both provided with lifestyle advice, in the management of treatment-naive men with moderately symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: 2-year CONDUCT study results. BJU Int. 2015;116:450–59. - PubMed
-
- Roehrborn CG, Siami P, Barkin J, Damiao R, Major-Walker K, Nandy I, Morrill BB, Gagnier RP, Montorsi F, Comb ATSG. The effects of combination therapy with dutasteride and tamsulosin on clinical outcomes in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: 4-year results from the CombAT study. Eur Urol. 2010;57:123–131. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.09.035. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

