A new method for identifying causal genes of schizophrenia and anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 27580934
- PMCID: PMC5007646
- DOI: 10.1038/srep32571
A new method for identifying causal genes of schizophrenia and anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity
Abstract
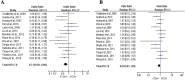
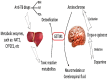
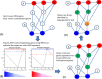
Schizophrenia (SCZ) may cause tuberculosis, the treatments for which can induce anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity (ATDH) and SCZ-like disorders. To date, the causal genes of both SCZ and ATDH are unknown. To identify them, we proposed a new network-based method by integrating network random walk with restart algorithm, gene set enrichment analysis, and hypergeometric test; using this method, we identified 500 common causal genes. For gene validation, we created a regularly updated online database ATDH-SCZgenes and conducted a systematic meta-analysis of the association of each gene with either disease. Till now, only GSTM1 and GSTT1 have been well studied with respect to both diseases; and a total of 23 high-quality association studies were collected for the current meta-analysis validation. Finally, the GSTM1 present genotype was confirmed to be significantly associated with both ATDH [Odds Ratio (OR): 0.71, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.56-0.90, P = 0.005] and SCZ (OR: 0.78, 95% CI: 0.66-0.92, P = 0.004) according to the random-effect model. Furthermore, these significant results were supported by "moderate" evidence according to the Venice criteria. Our findings indicate that GSTM1 may be a causal gene of both ATDH and SCZ, although further validation pertaining to other genes, such as CYP2E1 or DRD2, is necessary.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Meta-Analysis-Based Preliminary Exploration of the Connection between ATDILI and Schizophrenia by GSTM1/T1 Gene Polymorphisms.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 5;10(6):e0128643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128643. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26046920 Free PMC article.
-
CYP2E1, GSTM1 and GSTT1 genetic polymorphisms and susceptibility to antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: a nested case-control study.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2012 Oct;37(5):588-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2012.01334.x. Epub 2012 Feb 15. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2012. PMID: 22335459
-
Association of NAT2, GST and CYP2E1 polymorphisms and anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2014 May;94(3):293-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2014.02.003. Epub 2014 Feb 15. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2014. PMID: 24637014
-
Update meta-analysis of the CYP2E1 RsaI/PstI and DraI polymorphisms and risk of antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: evidence from 26 studies.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2016 Jun;41(3):334-40. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12388. Epub 2016 Apr 9. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2016. PMID: 27062377 Review.
-
Key factors of susceptibility to anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2015 Jun;89(6):883-97. doi: 10.1007/s00204-015-1473-1. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Arch Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25693865 Review.
Cited by
-
Implications of Newly Identified Brain eQTL Genes and Their Interactors in Schizophrenia.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018 Sep 7;12:433-442. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.05.026. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018. PMID: 30195780 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic polymorphisms and anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury: an umbrella review of the evidence.Int J Clin Pharm. 2025 Jun;47(3):624-639. doi: 10.1007/s11096-025-01880-9. Epub 2025 Feb 15. Int J Clin Pharm. 2025. PMID: 39954223
-
Glutathione S-Transferase M1/T1 Polymorphisms and Schizophrenia Risk: A New Method for Quality Assessment and a Systematic Review.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023 Jan 7;19:97-107. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S376942. eCollection 2023. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023. PMID: 36643584 Free PMC article.
-
Cross talk of chromosome instability, CpG island methylator phenotype and mismatch repair in colorectal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Aug;16(2):1736-1746. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8860. Epub 2018 May 31. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30008861 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying common genome-wide risk genes for major psychiatric traits.Hum Genet. 2020 Feb;139(2):185-198. doi: 10.1007/s00439-019-02096-4. Epub 2019 Dec 7. Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 31813014
References
-
- WHO. World Health Organization: Global tuberculosis report. (Date of access: 6/6/2015) (2012).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

