Wnt pathway regulation of intestinal stem cells
- PMID: 27581568
- PMCID: PMC5009769
- DOI: 10.1113/JP271754
Wnt pathway regulation of intestinal stem cells
Abstract
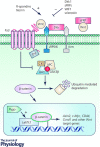
Wnt signalling is involved in multiple aspects of embryonic development and adult tissue homeostasis, notably via controlling cellular proliferation and differentiation. Wnt signalling is subject to stringent positive and negative regulation to promote proper development and homeostasis yet avoid aberrant growth. Such multi-layer regulation includes post-translational modification and processing of Wnt proteins themselves, R-spondin (Rspo) amplification of Wnt signalling, diverse receptor families, and intracellular and extracellular antagonists and destruction and transcription complexes. In the gastrointestinal tract, Wnt signalling is crucial for development and renewal of the intestinal epithelium. Intestinal stem cells (ISCs) undergo symmetric division and neutral drift dynamics to renew the intestinal epithelium. Sources of Wnts and Wnt amplifers such as R-spondins are beginning to be elucidated as well as their functional contribution to intestinal homeostasis. In this review we focus on regulation of ISCs and intestinal homeostasis by the Wnt/Rspo pathway, the potential cellular sources of Wnt signalling regulators and highlight potential future areas of study.
© 2016 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2016 The Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Aoki M, Mieda M, Ikeda T, Hamada Y, Nakamura H & Okamoto H (2007). R‐spondin3 is required for mouse placental development. Dev Biol 301, 218–226. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, Ridgway RA, van Es JH, van de Wetering M, Begthel H, van den Born M, Danenberg E, Clarke AR, Sansom OJ & Clevers H (2009). Crypt stem cells as the cells‐of‐origin of intestinal cancer. Nature 457, 608–611. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H, Peters PJ & Clevers H (2007). Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature 449, 1003–1007. - PubMed
-
- Bell SM, Schreiner CM, Wert SE, Mucenski ML, Scott WJ & Whitsett JA (2008). R‐spondin 2 is required for normal laryngeal‐tracheal, lung and limb morphogenesis. Development 135, 1049–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

