Comparison of Laparoscopic Microwave to Radiofrequency Ablation of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma (≤3 cm)
- PMID: 27581608
- PMCID: PMC5827943
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-016-5527-2
Comparison of Laparoscopic Microwave to Radiofrequency Ablation of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma (≤3 cm)
Abstract
Background: Laparoscopic thermal ablation is a common alternative to surgical resection in treating hepatic tumors, particularly in those located in difficult-to-reach locations.
Objective: The aim of this study was to compare the safety and long-term efficacy of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA) in treating hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Method: From February 2009 to May 2015, data from patients with HCC nodules who had undergone either laparoscopic MWA or laparoscopic RFA were examined. Complications, complete ablation rates, local tumor progression (LTP) rates, and disease-free and cumulative survival rates were compared between the two treatment groups.
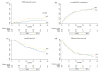
Results: A total of 154 patients with HCC (60 MWA and 94 RFA) were treated via the laparoscopic approach. Major complication rates were identified as 1 and 2 % in the RFA and MWA groups, respectively (p = 0.747). Complete ablation rates were 95 % for both treatment groups (p = 0.931), and LTP rates were 21.2 % for RFA and 8.3 % for MWA (p = 0.034). Disease-free survival rates at 5 years were 19 % in the RFA group and 12 % in the MWA group (p = 0.434), while cumulative survival rates at 5 years were 50 % in the RFA group and 37 % in the MWA group (p = 0.185).
Conclusion: Laparoscopic RFA and MWA appear to be safe in the treatment of early-stage HCC. The LTP rates were lower in the laparoscopic MWA group compared with the laparoscopic RFA group, but their respective overall and disease-free survival rates remained similar.
Figures
References
-
- Colombo M, Sangiovanni A. Treatment of hepatocellular caricnoma: beyond international guidelines. Liver Int. 2015;35(suppl 1):129–38. - PubMed
-
- Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M, Rolle E, Solbiati L, Tinelli C, Rossi S. Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology. 2008;47:82–89. - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–55. - PubMed
-
- De Lope CR, Tremosini S, Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Management of HCC. J Hepatol. 2012;56(suppl 1):S75–87. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Zhang J, Liu X, Li X, Jiao B, Kang T. Clinical outcomes of radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection for small hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27:51–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

